
Unlocking the Future: A Beginner’s Guide to Web3 Concepts & Applications
The internet as we know it is evolving, and at the forefront of this transformation is Web3. If you’ve heard terms like "blockchain," "NFTs," "DeFi," or "metaverse" and felt a little lost, you’re not alone. This comprehensive guide is designed to demystify Web3, breaking down its core concepts and showcasing its exciting real-world applications in a language anyone can understand.
Let’s dive into the internet’s next generation!
What is Web3? The Internet’s Next Evolution
To understand Web3, it’s helpful to look at how the internet has changed over time:
- Web1 (The Read-Only Web – roughly 1990s-early 2000s): This was the era of static websites. Think of it like a digital library where you could read information but not really interact or create content easily.
- Web2 (The Read-Write Web – roughly early 2000s-present): This is the internet most of us use today. It’s interactive, allowing us to create and share content on platforms like social media (Facebook, Twitter), video sites (YouTube), and marketplaces (Amazon, eBay). The catch? These platforms are centralized, meaning they are owned and controlled by large corporations. They host your data, dictate the rules, and can even censor content or deplatform users.
- Web3 (The Read-Write-Own Web – emerging now): This is the vision of a decentralized internet where users have more control and ownership. Instead of interacting with centralized companies, you interact directly with other users and applications built on open, distributed networks (like blockchains). In Web3, you truly own your data, digital assets, and even have a say in how platforms are governed.
In essence, Web3 aims to shift power from large corporations back to individual users.
Core Concepts That Define Web3
Web3 isn’t just one technology; it’s a collection of interconnected ideas and technologies working together. Here are the fundamental concepts:
1. Decentralization: No Single Point of Control
- The Idea: Imagine a giant spreadsheet that isn’t stored on one company’s server, but is instead copied and distributed across thousands of computers worldwide. No single entity owns or controls it. This is the essence of decentralization.
- How it Works: In Web3, information and applications are spread across a peer-to-peer network, rather than being managed by a central server. This makes them more resilient to censorship, outages, and manipulation.
- Why it Matters: It means no single company can unilaterally shut down a service, delete your data, or control what you see.
2. Blockchain Technology: The Backbone of Trust
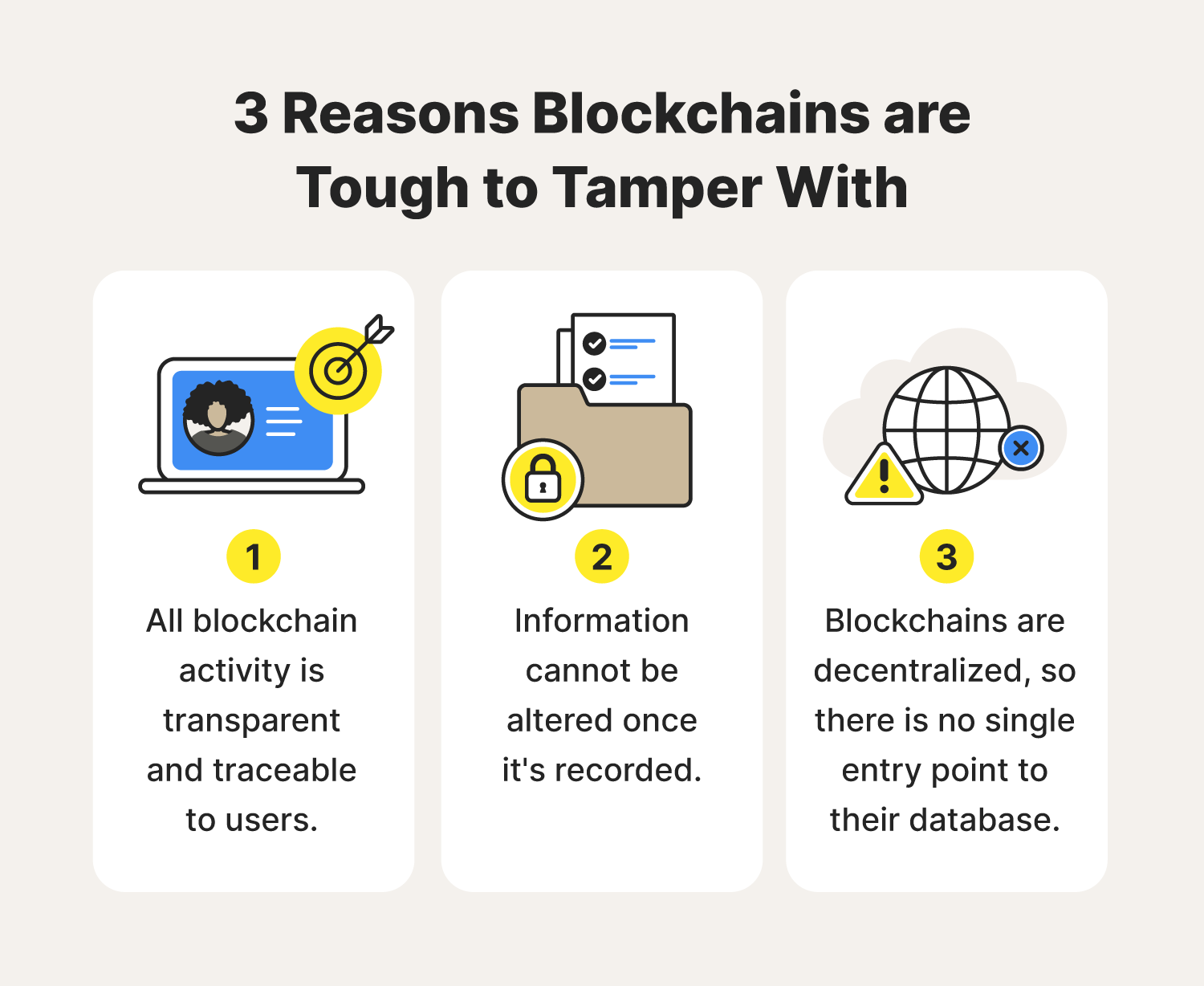
- The Idea: Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology (DLT). Think of it as a shared, unchangeable record book. Each "page" (block) contains a list of transactions, and once a page is filled, it’s added to the previous one, forming a "chain."
- How it Works:
- Immutable: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted.
- Transparent: All transactions are publicly visible (though often anonymous by default).
- Secure: Cryptographic techniques ensure the integrity and security of the data.
- Distributed: Copies of the ledger are maintained across many computers (nodes) on the network, making it highly resistant to attacks or single points of failure.
- Why it Matters: Blockchain provides the trust layer for Web3, allowing people to transact and interact without needing a central authority or intermediary.
3. User Ownership & Control: You Own Your Digital Self
- The Idea: In Web2, your data (photos, posts, personal info) is essentially "rented" from the platforms you use. In Web3, you truly own your digital assets and identity.
- How it Works: Through cryptographic keys and digital wallets, users gain direct ownership of their digital assets (like cryptocurrencies, NFTs) and control over their personal data.
- Why it Matters: This means you can port your data and identity across different applications, monetize your creations directly, and decide who accesses your information.
4. Permissionless & Trustless: Open and Fair Access
- Permissionless: Anyone can participate in Web3 networks without needing approval from a central authority. You don’t need to ask permission to build an application, send a transaction, or join a network.
- Trustless: Participants don’t need to trust a central intermediary. The rules of the network are enforced by code and cryptography, not by a company or government. You trust the code, not a person.
Key Technologies Powering Web3
These core concepts are brought to life by specific technologies:
1. Smart Contracts: Automated Agreements
- The Idea: Smart contracts are self-executing agreements written directly into lines of code. They run on a blockchain and automatically execute when predefined conditions are met.
- Analogy: Think of a vending machine. If you put in the correct money (condition met), the machine automatically dispenses your snack (action executed). No human intervention is needed.
- Why they Matter: Smart contracts automate processes, remove the need for intermediaries (like lawyers or banks in some cases), and ensure agreements are executed exactly as programmed. They are the building blocks for most Web3 applications.
2. Decentralized Applications (dApps): Apps on the Blockchain
- The Idea: dApps are applications that run on a decentralized peer-to-peer network (like a blockchain) instead of a single server. They use smart contracts for their backend logic.
- How they Differ from Regular Apps:
- Backend on Blockchain: No single company controls the server.
- Open Source: Their code is often publicly auditable.
- Token-Based Incentives: Often use cryptocurrencies or tokens to reward users or developers.
- Examples: Decentralized exchanges (DEXs), social media platforms, games.
3. Cryptocurrencies & Tokens: The Digital Fuel
- Cryptocurrencies: Digital or virtual currencies secured by cryptography, making them nearly impossible to counterfeit. They are decentralized, meaning they are not subject to government or financial institution control. Bitcoin and Ethereum are the most well-known.
- Tokens: Digital assets built on existing blockchain platforms (like Ethereum). They can represent various things:
- Utility Tokens: Give access to a dApp’s features or services.
- Governance Tokens: Give holders voting rights in a DAO (see below).
- Security Tokens: Represent ownership in a real-world asset or company.
- Why they Matter: They facilitate transactions, provide incentives, and enable new economic models within Web3 ecosystems.
4. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Unique Digital Assets
- The Idea: "Non-fungible" means unique and irreplaceable. An NFT is a unique digital certificate of ownership, stored on a blockchain, proving you own a specific digital item.
- Analogy: A dollar bill is "fungible" – any dollar bill is interchangeable with another. A specific painting, like the Mona Lisa, is "non-fungible" – it’s unique. An NFT is like the certificate of authenticity for a unique digital item.
- What they Represent: Digital art, music, collectibles, virtual land, in-game items, and even real-world assets.
- Why they Matter: NFTs enable true digital ownership, open up new possibilities for creators to monetize their work, and allow for verifiable scarcity in the digital realm.
5. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): Community-Led Governance
- The Idea: A DAO is an organization represented by rules encoded as a transparent computer program, controlled by the organization’s members, and not influenced by a central government.
- How it Works: Members (who often hold governance tokens) vote on proposals to manage the organization’s treasury, update its rules, or make other key decisions. The votes are recorded on the blockchain, and decisions are executed automatically by smart contracts.
- Why they Matter: DAOs offer a new, transparent, and democratic way to organize and manage projects, communities, and even companies, aligning incentives among all participants.
Real-World Applications of Web3
Web3 is not just theoretical; it’s already powering innovative applications across various sectors:
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Banking Without Banks
- Concept: Recreating traditional financial services (lending, borrowing, trading, insurance) using smart contracts on blockchains, without the need for intermediaries like banks.
- Examples:
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Trade cryptocurrencies directly with other users (e.g., Uniswap, PancakeSwap).
- Lending/Borrowing Platforms: Lend your crypto to earn interest or borrow crypto by providing collateral (e.g., Aave, Compound).
- Benefits: Open access (anyone with an internet connection can participate), lower fees, faster transactions, transparency.
2. Gaming (GameFi & Play-to-Earn): True Ownership & Rewards
- Concept: Integrating blockchain technology into video games, allowing players to truly own in-game assets (as NFTs) and even earn cryptocurrency by playing.
- Examples:
- Axie Infinity: Players collect, breed, and battle NFT creatures, earning tokens.
- The Sandbox / Decentraland: Virtual worlds where players can buy, build on, and monetize virtual land (NFTs).
- Benefits: Players own their digital items, can trade them on open marketplaces, and can potentially earn income from their gaming activities.
3. Metaverse: Immersive Digital Worlds
- Concept: Interconnected virtual worlds where users can interact with each other, digital objects, and AI in real-time. Web3 principles are crucial for making the metaverse truly decentralized and user-owned.
- Web3 Connection: NFTs represent virtual land, avatars, and items. Cryptocurrencies are used for transactions. DAOs can govern virtual communities.
- Benefits: New forms of social interaction, commerce, entertainment, and work in digital spaces, with user ownership at its core.
4. Digital Identity & Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI): Your Identity, Your Control
- Concept: Giving individuals complete control over their digital identities and personal data, rather than relying on centralized entities (like Google or Facebook) to manage it.
- How it Works: Users create verifiable credentials on the blockchain, choosing exactly what information to share and with whom.
- Benefits: Enhanced privacy, reduced risk of identity theft, and a portable digital identity that can be used across various platforms without re-entering data or trusting third parties.
5. Supply Chain Management: Transparency & Traceability
- Concept: Using blockchain to create a transparent and immutable record of a product’s journey from raw materials to the consumer.
- How it Works: Each step in the supply chain (manufacturing, shipping, delivery) can be recorded on a blockchain, ensuring authenticity and traceability.
- Benefits: Combats counterfeiting, improves product safety, helps verify ethical sourcing, and increases consumer trust.
6. Creator Economy: Direct Monetization & Fan Engagement
- Concept: Empowering creators (artists, musicians, writers, content creators) to connect directly with their audience and monetize their work without relying on intermediaries that take a large cut.
- How it Works: NFTs allow creators to sell unique digital assets directly to fans. Fan tokens enable direct engagement and shared governance.
- Benefits: Fairer compensation for creators, stronger community building, and new ways for fans to support and participate in their favorite creators’ journeys.
The Benefits of Web3
- Enhanced Security & Transparency: Blockchain’s immutable and distributed nature makes transactions and data highly secure and auditable.
- User Empowerment: Users gain control over their data, identity, and digital assets, reducing reliance on centralized corporations.
- Censorship Resistance: Decentralized networks are much harder for any single entity to control or shut down, promoting free speech and open access.
- New Economic Models: Play-to-earn, creator monetization, and DeFi open up novel ways for individuals to earn, transact, and participate in the digital economy.
- Interoperability: The vision of Web3 aims for seamless movement of assets and identity across different applications and platforms.
Challenges and Considerations for Web3
While the potential of Web3 is immense, it’s still in its early stages and faces several hurdles:
- Scalability: Current blockchain networks can be slow and expensive compared to traditional systems, making it difficult to handle mass adoption.
- User Experience (UX): Web3 applications can be complex and intimidating for beginners, requiring knowledge of wallets, seed phrases, and gas fees.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments worldwide are still grappling with how to regulate cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and other Web3 technologies, leading to a lack of clear guidelines.
- Environmental Concerns: Some blockchain networks (particularly those using "Proof-of-Work" like older Ethereum and Bitcoin) consume significant energy, though "Proof-of-Stake" and other solutions are addressing this.
- Security Risks: While the underlying blockchain is secure, smart contract bugs, phishing scams, and user error (losing private keys) can still lead to financial losses.
Conclusion: A Glimpse into the Future
Web3 represents a fundamental shift in how we interact with the internet. By leveraging decentralization, blockchain, and smart contracts, it promises a more open, transparent, and user-centric digital world. While it’s still an evolving space with its own set of challenges, the core concepts of ownership, control, and permissionless innovation are powerful.
As more developers build, and more users explore, Web3 is poised to reshape industries, empower individuals, and unlock new possibilities for how we live, work, and play online. It’s an exciting time to learn and engage with the internet’s next frontier!


Post Comment