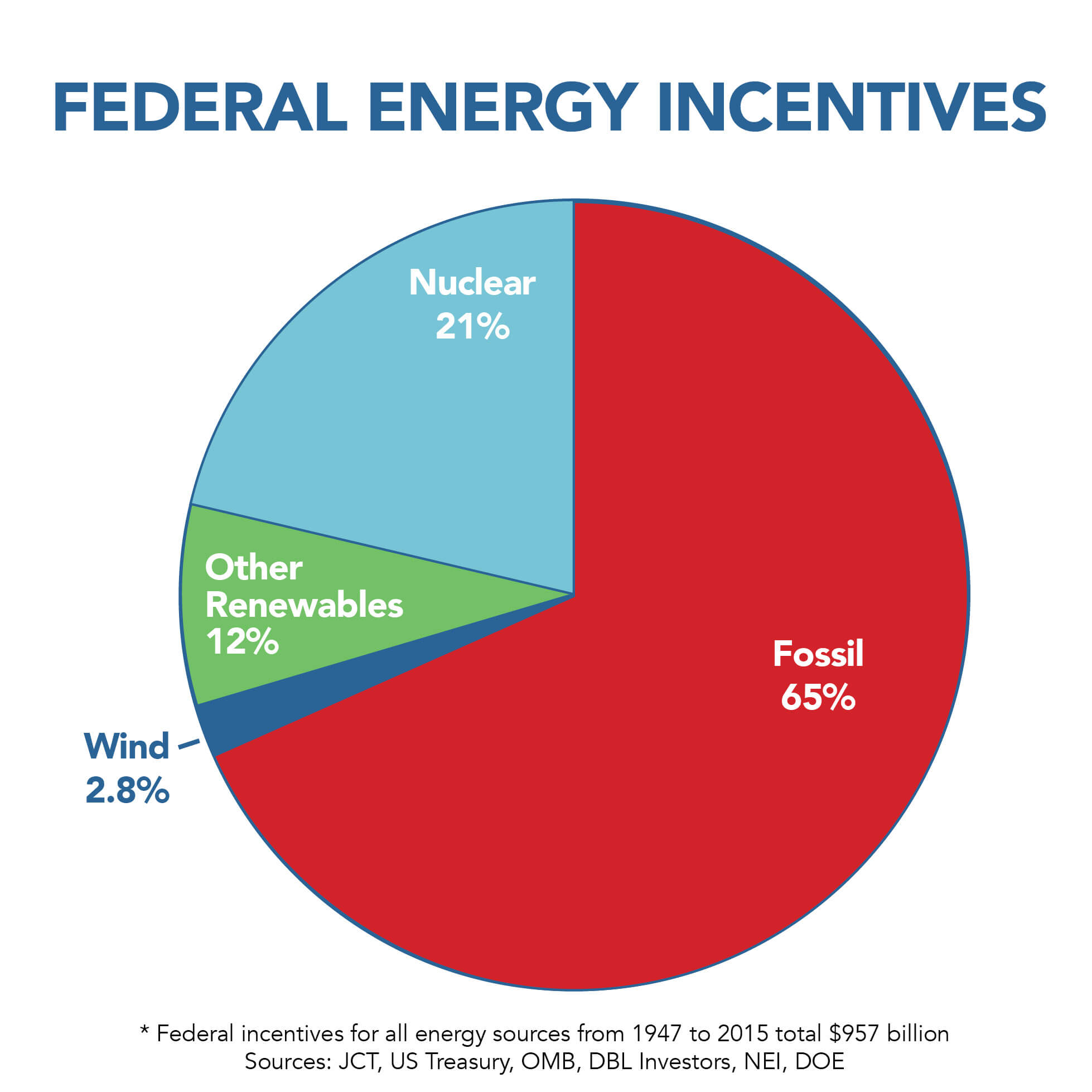
Unlocking Green Power: A Beginner’s Guide to Government Incentives for Renewable Energy Adoption
Imagine a world powered by clean, endless energy. A world where your electricity comes from the sun on your roof, the wind in the fields, or the warmth deep within the Earth. This isn’t a distant dream; it’s a rapidly growing reality, and governments around the globe are playing a huge role in making it happen.
While the idea of switching to renewable energy like solar panels or wind turbines is exciting, the initial cost can sometimes feel like a barrier. That’s where government incentives come in! These aren’t handouts; they’re smart investments by governments to accelerate our transition to a cleaner, more sustainable future.
This comprehensive guide will demystify government incentives for renewable energy adoption, explaining what they are, why they exist, and how you – whether you’re a homeowner, a business owner, or part of a community – can potentially benefit.
Why Do Governments Offer Renewable Energy Incentives?
It might seem like a lot of money for governments to put towards new energy sources. However, the reasons behind these incentives are compelling and benefit everyone in the long run:
- Combating Climate Change: This is arguably the biggest driver. Renewable energy sources produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions, which are responsible for global warming. By encouraging their adoption, governments aim to reduce carbon footprints and meet international climate goals.
- Boosting Energy Independence & Security: Relying heavily on fossil fuels often means depending on other countries for energy. Renewable energy, generated domestically, reduces this reliance, making nations more energy secure and less vulnerable to global price fluctuations.
- Creating Green Jobs & Economic Growth: The renewable energy sector is a massive job creator, from manufacturing and installation to research and development. Incentives stimulate this industry, leading to economic growth and new opportunities.
- Improving Public Health: Burning fossil fuels releases pollutants into the air, contributing to respiratory diseases and other health issues. Clean energy sources improve air quality, leading to healthier communities.
- Driving Innovation: Incentives often include funding for research and development (R&D), pushing the boundaries of renewable energy technology, making it more efficient and affordable over time.
- Stabilizing Energy Prices: Once installed, renewable energy systems like solar panels have predictable, often zero, fuel costs. This can help stabilize long-term energy prices for consumers and businesses.
Types of Government Incentives for Renewable Energy
Government incentives come in various shapes and sizes, designed to help different types of projects and individuals. Here are the most common ones you’ll encounter:
1. Tax Credits
What they are: This is one of the most popular and straightforward incentives. A tax credit directly reduces the amount of income tax you owe. It’s not a deduction (which reduces your taxable income), but a dollar-for-dollar reduction in your actual tax bill.
- How it works: If you owe $5,000 in taxes and qualify for a $2,000 tax credit, your tax bill drops to $3,000.
- Who benefits: Primarily homeowners and businesses installing renewable energy systems (like solar panels, wind turbines, geothermal systems) on their property.
- Key features:
- Often a percentage of the total system cost (e.g., 30% of the cost of your solar installation).
- Can sometimes be carried forward if you don’t use the full amount in one year.
- Available at federal, state, and sometimes local levels.
2. Rebates
What they are: A rebate is a direct payment or discount given to you after you purchase and install a qualifying renewable energy system. It’s essentially money back in your pocket.
- How it works: You buy and install your solar panels, then submit proof of purchase and installation to the government agency or utility offering the rebate. They send you a check or apply a credit to your bill.
- Who benefits: Homeowners, businesses, and sometimes communities.
- Key features:
- Can be a fixed amount per system, or based on the system’s capacity (e.g., "$X per kilowatt-hour").
- Often offered by state or local governments, or even utility companies.
- Funds can be limited, so they might be on a first-come, first-served basis.
3. Grants
What they are: Grants are funds provided by governments or organizations that do not need to be repaid, typically given for specific projects that align with their goals.
- How it works: You apply for a grant with a detailed proposal outlining your renewable energy project. If approved, you receive the funds to execute the project.
- Who benefits: More common for non-profits, educational institutions, government entities, or businesses undertaking innovative R&D projects, community-scale renewable projects, or projects in underserved areas. Less common for individual homeowners.
- Key features:
- Highly competitive.
- Often have strict eligibility criteria and reporting requirements.
- Can fund significant portions of a project’s cost, including research, development, and deployment.
4. Low-Interest Loans & Loan Programs
What they are: These programs offer financing for renewable energy projects at interest rates significantly lower than market rates, making the investment more affordable.
- How it works: You apply for a loan through a specific government-backed program or partner financial institution. The lower interest rate reduces your monthly payments and overall cost of borrowing.
- Who benefits: Homeowners, small businesses, and agricultural operations.
- Key features:
- Can make the upfront cost of renewable energy systems much more manageable.
- May have flexible repayment terms.
- Often offered by state or local energy agencies, or through federal programs targeting specific sectors (e.g., rural development).
5. Feed-in Tariffs (FITs)
What they are: FITs are policies that guarantee a fixed, above-market price for electricity generated from renewable sources and fed into the national grid.
- How it works: If you have a solar or wind system that produces more electricity than you use, the utility company buys that excess power from you at a premium rate set by the government.
- Who benefits: Homeowners, businesses, and community projects that generate excess electricity.
- Key features:
- Encourages investment by providing a stable and attractive return on electricity generation.
- Contracts typically last for a fixed period (e.g., 10-20 years).
- More common in some countries than others (e.g., Germany has a strong history with FITs).
6. Net Metering
What they are: Net metering is a billing mechanism that allows consumers who generate their own electricity (e.g., with solar panels) to send excess power back to the grid and receive credit on their electricity bill.
- How it works: Your electricity meter essentially runs backward when you’re producing more power than you’re consuming. You only pay for your "net" electricity consumption (total consumed minus total generated).
- Who benefits: Primarily homeowners and businesses with grid-tied renewable energy systems.
- Key features:
- Crucial for making small-scale renewable energy economically viable.
- Policies vary widely by state and utility company, including credit rates and whether credits roll over month-to-month.
7. Property Assessed Clean Energy (PACE) Programs
What they are: PACE programs allow property owners to finance energy efficiency and renewable energy improvements on their homes or businesses, repaying the costs through an assessment on their property tax bill.
- How it works: The cost of the improvements is added to your property taxes. If you sell your property, the remaining assessment often transfers to the new owner.
- Who benefits: Homeowners and commercial property owners in participating areas.
- Key features:
- Can cover 100% of the project cost.
- Repayment terms can be long (e.g., 10-20 years).
- Availability depends on local government adoption.
8. Research & Development (R&D) Funding
What they are: Governments invest heavily in R&D to advance renewable energy technologies, making them more efficient, cost-effective, and versatile.
- How it works: Funding is provided to universities, private companies, and national labs to conduct cutting-edge research in areas like battery storage, advanced solar materials, offshore wind technology, and smart grid solutions.
- Who benefits: Researchers, scientists, technology companies, and the entire energy sector through technological breakthroughs.
Who Can Benefit from These Incentives?
The beauty of government incentives is their broad reach. While specific programs vary, many different groups can benefit:
- Homeowners: Looking to reduce electricity bills, increase property value, and shrink their carbon footprint.
- Businesses (Small & Large): Aiming to lower operating costs, meet sustainability goals, and enhance their brand image.
- Farmers & Agricultural Operations: Seeking to reduce energy expenses for irrigation, heating, and processing, often through specialized rural development programs.
- Non-Profits & Community Organizations: Wanting to power community centers, schools, or develop local renewable energy projects.
- Municipalities & Public Entities: Investing in clean energy for public buildings, streetlights, and city-wide initiatives.
- Renewable Energy Developers & Installers: These companies are often crucial in helping others access incentives and grow the green economy.
How to Find and Access Government Incentives
Navigating the world of incentives can seem daunting, but it’s manageable with a systematic approach:
-
Start with Your Location: Incentives vary significantly by country, state, county, and even city.
- Federal/National Level: Look for nationwide programs (e.g., the Investment Tax Credit for solar in the U.S.).
- State/Provincial Level: Many states have their own robust incentive programs (rebates, loan programs, renewable energy targets).
- Local/Municipal Level: Your city or county might offer specific property tax exemptions, permitting fee reductions, or local grants.
- Utility Companies: Don’t forget your local electricity provider! Many utilities offer their own rebates or net metering programs.
-
Utilize Online Databases: Several excellent resources compile incentive information:
- DSIRE (Database of State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency): For the U.S., DSIRE is an incredibly comprehensive resource detailing federal, state, and local incentives.
- Government Energy Websites: Official government energy department websites are key. Search for "renewable energy incentives [your country/state/city]".
- International Energy Agency (IEA) or IRENA: These organizations provide global overviews and links to national policies.
-
Consult with Energy Professionals:
- Certified Solar Installers, Wind Turbine Companies, Geothermal Specialists: Reputable companies in the renewable energy sector are often highly knowledgeable about available incentives and can help you navigate the application process. They frequently factor incentives into their quotes.
- Energy Auditors/Consultants: These professionals can assess your specific needs and recommend the most beneficial incentives.
-
Understand Eligibility & Requirements:
- System Type: Ensure your chosen renewable energy system qualifies.
- Installation Date: Some incentives are time-sensitive.
- Certifications: Ensure installers and equipment meet necessary standards.
- Income/Business Size: Some programs target specific income levels or business types.
- Application Process: Be prepared for paperwork, deadlines, and potential inspections.
The Broader Impact: Beyond Your Wallet
While the financial savings are a huge motivator, remember that leveraging government incentives for renewable energy contributes to a much larger positive impact:
- Accelerating the Green Transition: Every solar panel installed, every wind turbine erected, pushes us closer to a world less reliant on fossil fuels.
- Building Resilient Communities: Local energy generation makes communities more resilient to power outages and global energy crises.
- Fostering Innovation: Demand for renewable energy drives further investment in R&D, leading to even better, cheaper technologies in the future.
- Creating a Legacy: By adopting renewable energy, you’re not just saving money; you’re investing in a healthier, more sustainable planet for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Are these incentives only for large companies, or can homeowners apply?
A: Absolutely not! Many of the most popular incentives, like federal tax credits and state rebates, are specifically designed for individual homeowners.
Q2: Do incentives cover all types of renewable energy?
A: Most commonly, incentives cover solar PV (photovoltaic), solar water heating, wind turbines, and geothermal systems. Some programs may also include biomass, fuel cells, and small-scale hydropower. Always check the specific program’s details.
Q3: How long do these incentives last? Are they permanent?
A: No, incentives are often temporary or have expiration dates. Governments review and adjust them based on market conditions, policy goals, and budget availability. It’s crucial to act while programs are active.
Q4: Can I combine multiple incentives?
A: Often, yes! For example, you might be able to combine a federal tax credit with a state rebate and a local property tax exemption. However, some programs may have rules against stacking certain incentives, so always check the fine print.
Q5: Where should I start if I’m interested?
A: A great starting point is to contact reputable local renewable energy installers. They often have the most up-to-date information on available incentives in your area and can guide you through the process. You can also visit your country’s main energy department website or dedicated incentive databases like DSIRE (for the U.S.).
Conclusion
Government incentives are powerful tools that bridge the gap between the upfront cost of renewable energy and its long-term benefits. By understanding and utilizing these programs, individuals, businesses, and communities can play a direct role in accelerating the transition to a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
Don’t let the initial investment deter you from exploring renewable energy. With the right information and a bit of research, you might find that going green is not only good for the planet but also incredibly smart for your wallet. Start your journey today – the incentives are there to help power your green dreams!


Post Comment