The Transformative Power: The Impact of AI on the Global Economy
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept from science fiction; it’s a powerful force rapidly reshaping our world, and nowhere is its influence more profound than on the global economy. From the way we work and shop to how businesses operate and innovate, AI is driving changes that are both exciting and challenging.
But what exactly is AI, and how is it impacting something as vast and complex as the global economy? This article will break down the key ways AI is making its mark, in language that’s easy for everyone to understand.
What Exactly is AI? (The Basics for Beginners)
Before we dive into its economic impact, let’s quickly define AI.
Imagine teaching a computer to "think" or "learn" like a human, but much faster and with access to far more information. That’s essentially what AI aims to do.
In simple terms, AI refers to computer systems designed to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as:
- Learning: Adapting to new information and improving over time.
- Reasoning: Solving problems and making decisions.
- Perception: Understanding images, sounds, and language.
- Problem-solving: Finding solutions to complex challenges.
Think of AI as the "brain" behind many of today’s smart technologies – from the recommendation engine on your favorite streaming service to the sophisticated algorithms guiding self-driving cars.
AI’s Role in Boosting Productivity and Efficiency
One of the most immediate and significant impacts of AI on the economy is its ability to supercharge productivity and efficiency across almost every sector.
How AI helps businesses do more with less:
- Automation of Repetitive Tasks: AI-powered robots and software can handle mundane, repetitive jobs much faster and more accurately than humans. This includes tasks like data entry, customer service inquiries (chatbots), assembly line work, and even basic accounting.
- Benefit: Frees up human workers to focus on more complex, creative, and strategic tasks.
- Enhanced Data Analysis: We live in a world overflowing with data. AI can process, analyze, and find patterns in massive datasets in seconds – something impossible for humans.
- Benefit: Businesses can make smarter decisions based on real insights, leading to better products, more targeted marketing, and optimized operations.
- Optimized Resource Management: AI can predict demand, manage supply chains, and optimize energy consumption.
- Benefit: Reduces waste, lowers operational costs, and improves delivery times for goods and services.
- Personalization at Scale: AI can analyze individual preferences and behaviors to offer highly personalized experiences, from product recommendations in e-commerce to customized educational content.
- Benefit: Increases customer satisfaction and sales.
Examples in Action:
- Manufacturing: AI-driven robots work alongside humans, improving production speed and quality.
- Healthcare: AI helps analyze medical images (like X-rays) to detect diseases earlier and more accurately.
- Finance: AI systems detect fraudulent transactions in real-time, protecting consumers and banks.
- Retail: AI personalizes shopping experiences and manages inventory to prevent stockouts.
The AI Impact on the Job Market: Fear vs. Reality
This is perhaps the most talked-about and often feared aspect of AI’s economic impact: its effect on jobs. Will robots take all our jobs? The reality is more nuanced.
1. Job Displacement (The Loss of Certain Jobs):
It’s true that AI and automation will displace some jobs, particularly those that are highly repetitive, predictable, and require low-level cognitive skills.
- Examples of jobs at risk:
- Certain manufacturing roles
- Data entry clerks
- Telemarketers
- Some administrative support roles
- Truck drivers (with autonomous vehicles)
2. Job Creation (The Rise of New Jobs):
While some jobs disappear, AI also creates entirely new categories of jobs and enhances existing ones. These new roles often require skills that complement AI, rather than compete with it.
- Examples of jobs created/enhanced by AI:
- AI Researchers & Engineers: People who design, build, and maintain AI systems.
- Data Scientists & Analysts: Experts who work with the vast amounts of data AI uses.
- AI Ethicists & Policy Makers: Professionals who ensure AI is developed and used responsibly and fairly.
- Prompt Engineers: People skilled at crafting the right instructions for AI models to get desired outputs.
- Robot Maintenance Technicians: People who repair and maintain automated machinery.
- Creativity-focused roles: Jobs that emphasize human skills like critical thinking, emotional intelligence, negotiation, and artistic creation, which AI struggles to replicate.
3. The Importance of Reskilling and Upskilling:
The biggest challenge isn’t necessarily a net loss of jobs, but a shift in the types of skills needed. To thrive in the AI economy, workers will need to adapt.
- Lifelong Learning: Continuously acquiring new skills will be crucial.
- Focus on "Human" Skills: Emphasize creativity, critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, and emotional intelligence – skills that AI cannot easily replicate.
- Collaboration with AI: Learning to work with AI tools, using them to enhance human capabilities, will be a key skill.
AI as a Driver of New Industries and Innovation
Beyond improving existing industries, AI is a powerful engine for creating entirely new ones and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
How AI fuels economic growth through innovation:
- Emergence of the AI Industry Itself: The development, deployment, and maintenance of AI systems form a massive new industry, attracting billions in investment and creating thousands of high-paying jobs.
- Transforming Existing Sectors: AI is revolutionizing fields that have been around for centuries:
- Healthcare: Accelerating drug discovery, personalizing treatments, and improving diagnostics.
- Agriculture: Enabling "precision farming" to optimize crop yields and reduce waste.
- Energy: Managing smart grids and optimizing renewable energy sources.
- Transportation: Powering autonomous vehicles and intelligent traffic management systems.
- New Products and Services: AI enables the creation of products and services that were once unimaginable, from personalized learning platforms to advanced virtual assistants and smart home devices.
- Increased Research & Development (R&D): The competition to develop cutting-edge AI drives massive investment in R&D, leading to breakthroughs that benefit the entire economy.
This innovation translates directly into economic growth, new market opportunities, and improved quality of life.
Investment, Capital, and GDP Growth
The economic impact of AI isn’t just theoretical; it’s being measured in billions and trillions of dollars.
- Massive Investment: Companies, governments, and venture capitalists are pouring enormous sums into AI research, development, and adoption. This investment stimulates economic activity.
- Increased Productivity Leading to GDP Growth: When businesses become more efficient and productive through AI, they can produce more goods and services with the same or fewer resources. This directly contributes to a nation’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP), which is the total value of goods and services produced in a country.
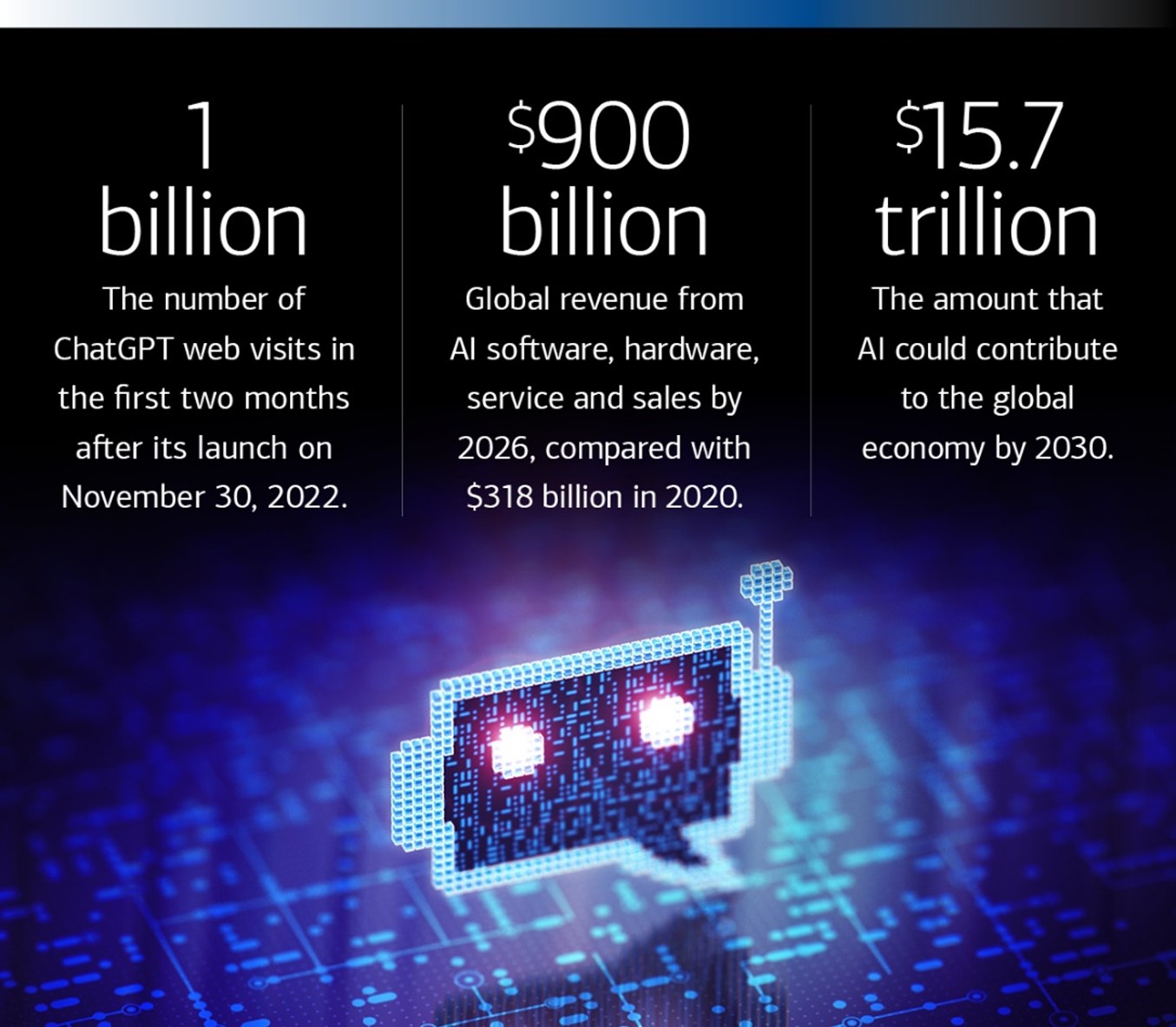
- Forecasts: Many economic reports predict that AI could add trillions of dollars to global GDP over the next decade. For example, PwC estimates AI could contribute up to $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030.
- New Revenue Streams: AI-powered products and services open up new markets and generate new revenue streams for businesses.
- Competitive Advantage: Nations and companies that embrace AI gain a significant competitive edge in the global marketplace, attracting more investment and talent.
The Challenges and Risks of AI’s Economic Impact
While the benefits are substantial, it’s crucial to acknowledge the potential downsides and challenges that AI presents to the global economy.
1. Economic Inequality:
- The "Haves" and "Have-Nots": If the benefits of AI are concentrated among a small group of highly skilled workers, tech companies, and investors, it could widen the gap between the rich and the poor.
- Digital Divide: Countries or regions with less access to technology, education, and infrastructure might fall further behind, exacerbating global economic disparities.
- Wage Stagnation: For jobs that are not directly displaced but are easily augmented by AI, there might be downward pressure on wages as AI tools make fewer human workers necessary for the same output.
2. Ethical Concerns and Bias:
- Algorithmic Bias: AI systems learn from the data they’re fed. If this data contains historical biases (e.g., in hiring or lending), the AI can perpetuate and even amplify those biases, leading to unfair outcomes.
- Privacy Issues: AI relies on vast amounts of data, raising concerns about individual privacy and how personal information is collected, stored, and used.
- Accountability: Who is responsible when an AI system makes a mistake or causes harm? Defining legal and ethical accountability for AI actions is complex.
3. Cybersecurity Risks:
- AI can be used by malicious actors to create more sophisticated cyberattacks (e.g., highly realistic phishing scams, automated hacking).
- The increasing interconnectedness of AI systems creates new vulnerabilities for critical infrastructure.
4. Regulatory Lag:
- Technology often moves faster than laws and regulations. Governments around the world are struggling to keep up with the rapid pace of AI development, leading to a lack of clear guidelines for its ethical and safe deployment.
5. Monopoly Power:
- A few large tech companies currently dominate AI research and development. This concentration of power could lead to monopolies, stifling competition and innovation in the long run.
Preparing for the AI Economy: A Collective Effort
Successfully navigating the AI revolution requires proactive measures from individuals, businesses, and governments.
1. For Individuals:
- Embrace Lifelong Learning: Continuously learn new skills, especially those that complement AI (e.g., data literacy, critical thinking, creativity).
- Focus on "Human-Centric" Skills: Develop communication, collaboration, emotional intelligence, and ethical reasoning.
- Adaptability: Be open to career changes and new ways of working.
2. For Businesses:
- Invest in AI Adoption: Explore how AI can enhance operations, products, and services.
- Reskill and Upskill Your Workforce: Provide training programs to help employees adapt to AI tools and new roles.
- Foster an Innovative Culture: Encourage experimentation and collaboration between humans and AI.
- Prioritize Ethical AI: Develop and deploy AI responsibly, considering fairness, transparency, and accountability.
3. For Governments and Policymakers:
- Invest in Education and Training: Fund programs that prepare the workforce for AI-era jobs.
- Develop Robust Regulatory Frameworks: Create clear laws and guidelines for AI development and use, addressing ethics, privacy, and safety.
- Support Research and Development: Fund basic and applied AI research to maintain a competitive edge.
- Implement Social Safety Nets: Consider policies like universal basic income or robust unemployment benefits to support workers displaced by automation during the transition.
- Promote Fair Competition: Prevent monopolies and encourage a diverse AI ecosystem.
Conclusion: A Future Shaped by Choice
The impact of AI on the global economy is monumental and undeniable. It promises unprecedented productivity gains, fuels innovation, and opens up new avenues for growth that could elevate living standards worldwide. However, it also presents significant challenges, particularly regarding job displacement, economic inequality, and ethical dilemmas.
The future of the AI economy isn’t predetermined. It will be shaped by the choices we make today – as individuals, businesses, and governments. By embracing continuous learning, fostering responsible innovation, and implementing thoughtful policies, we can harness the transformative power of AI to create a more prosperous, efficient, and equitable global economy for everyone. The journey ahead will be complex, but the opportunity to build a better future with AI is within our grasp.



Post Comment