
Beyond Bitcoin: Unpacking Blockchain Use Cases for a Decentralized Future
When you hear the word "blockchain," what’s the first thing that comes to mind? For many, it’s Bitcoin, Ethereum, and the volatile world of cryptocurrencies. While digital currencies are certainly blockchain’s most famous application, they represent just the tip of a vast and transformative iceberg. Blockchain technology, at its core, is a revolutionary way to record and share information in a secure, transparent, and unchangeable manner.
Imagine a digital ledger that isn’t controlled by any single entity, is incredibly difficult to tamper with, and is updated in real-time for all authorized participants to see. That’s blockchain in a nutshell. This distributed ledger technology (DLT) is poised to reshape industries far beyond finance, offering solutions to long-standing challenges in areas like trust, transparency, efficiency, and data security.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the fascinating world of blockchain use cases that extend far beyond its cryptocurrency origins. We’ll explore how this technology is building a more secure, efficient, and equitable future for everyone, one block at a time.
Understanding the Core Principles: Why Blockchain Matters
Before we explore its applications, let’s briefly touch upon the fundamental characteristics that make blockchain so powerful and unique:
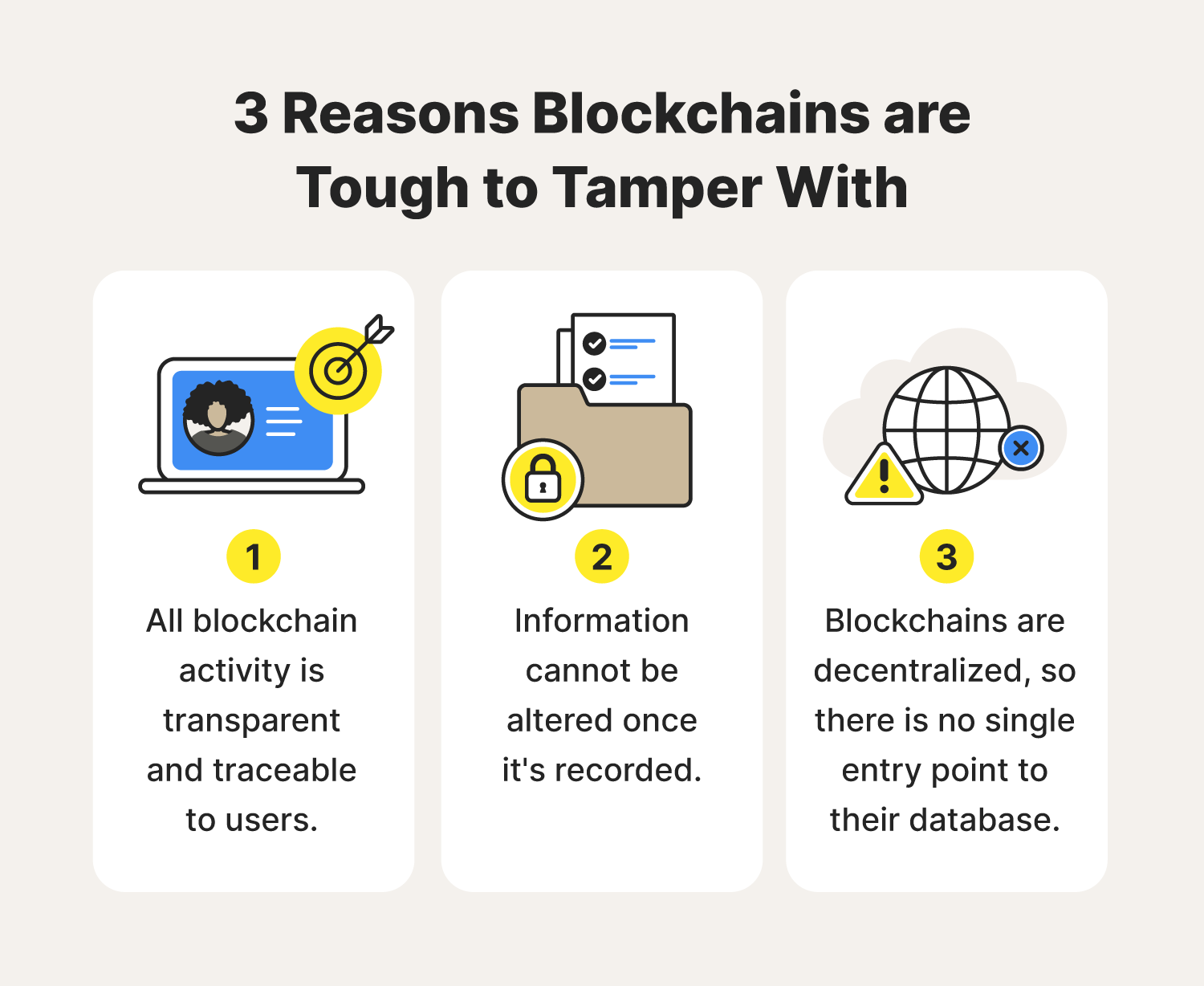
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional systems where a central authority (like a bank or government) controls all data, blockchain distributes the ledger across a network of computers. This eliminates single points of failure and reduces the risk of manipulation.
- Immutability: Once a transaction or piece of data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. Each "block" of information is cryptographically linked to the previous one, forming an unbreakable chain. This creates an unchangeable audit trail.
- Transparency (Selective): While the identities of participants can be pseudonymous, the transactions themselves are often transparent and verifiable by anyone on the network. This fosters trust and accountability.
- Security: Cryptographic techniques are used to secure transactions and verify identities, making it highly resistant to fraud and unauthorized access.
- Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. They automatically execute when predefined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries and speeding up processes.
These core principles unlock a world of possibilities for industries seeking to enhance trust, streamline operations, and safeguard data.
Blockchain Use Cases Beyond Cryptocurrency
Let’s explore the exciting real-world applications of blockchain technology that are already making a significant impact or show immense promise for the future.
1. Supply Chain Management & Logistics
One of the most compelling applications of blockchain is in transforming complex supply chains. From farm to factory, and factory to consumer, tracking goods can be incredibly challenging, leading to inefficiencies, fraud, and a lack of transparency.
How Blockchain Helps:
- Enhanced Traceability: Every step of a product’s journey – from raw materials to manufacturing, shipping, and delivery – can be recorded on the blockchain. This creates an immutable and transparent record, allowing all participants (manufacturers, distributors, retailers, consumers) to see the origin and journey of goods.
- Example: Tracking premium coffee beans from the specific farm they were grown on, through processing, shipping, and finally to your local cafe, ensuring fair trade practices and authenticity.
- Fraud Prevention: Counterfeit goods are a massive problem globally. Blockchain can verify the authenticity of products by providing a digital fingerprint that can be checked by consumers.
- Improved Efficiency: Automated smart contracts can trigger payments or release goods once certain conditions (e.g., arrival at a port, quality check completion) are met, speeding up processes and reducing manual errors.
- Food Safety: In the event of a recall, blockchain can quickly pinpoint the exact source of contamination, limiting the scope of the recall and protecting consumers.
2. Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals
The healthcare industry grapples with fragmented patient data, privacy concerns, drug counterfeiting, and complex administrative processes. Blockchain offers a promising path to address these challenges.
How Blockchain Helps:
- Secure Patient Records: Blockchain can create an unchangeable, encrypted record of a patient’s medical history. Patients could control who has access to their data, granting temporary permissions to doctors, specialists, or researchers, thereby improving interoperability and data privacy.
- Drug Authenticity & Supply Chain: Tracking pharmaceuticals from production to pharmacy ensures the integrity of medications, combating the global issue of counterfeit drugs and preventing diversion.
- Clinical Trials Management: Blockchain can record and timestamp trial data, ensuring its integrity and immutability, which is crucial for regulatory compliance and scientific validity.
- Insurance Claims Processing: Smart contracts can automate the verification and processing of insurance claims, reducing administrative overhead and speeding up payouts.
3. Digital Identity & Data Security
In an increasingly digital world, managing and securing our online identities is paramount. Blockchain offers a path toward self-sovereign identity, giving individuals more control over their personal data.
How Blockchain Helps:
- Self-Sovereign Identity: Individuals can store their verifiable credentials (e.g., driver’s license, passport, educational degrees) on a blockchain-based identity system. They then choose which pieces of information to share with whom, without relying on a central authority.
- Example: Instead of giving a website your full date of birth, you could simply prove you are over 18 using a verifiable credential stored on the blockchain, without revealing unnecessary personal details.
- Secure Authentication: Blockchain can power more secure login systems, reducing reliance on easily hackable passwords.
- KYC (Know Your Customer) & AML (Anti-Money Laundering): Financial institutions can use blockchain to share verified customer identities securely, streamlining compliance processes and reducing redundant checks across different organizations.
4. Real Estate & Property Management
The real estate industry is often slow, opaque, and laden with intermediaries and paperwork. Blockchain can inject transparency, efficiency, and trust.
How Blockchain Helps:
- Streamlined Property Transfers: Recording property titles and ownership changes on a blockchain can eliminate lengthy processes, reduce fraud, and provide an immutable record of ownership.
- Fractional Ownership: Blockchain and smart contracts enable the tokenization of real estate, allowing multiple investors to own a fraction of a property. This lowers the barrier to entry for real estate investment.
- Land Registry: Creating a secure, unchangeable digital land registry can prevent disputes, reduce corruption, and make property ownership more transparent.
- Automated Payments: Smart contracts can automate rent payments or the release of funds upon the fulfillment of lease agreements.
5. Voting & Governance
While still in its early stages, blockchain holds the potential to revolutionize electoral processes and organizational governance by enhancing transparency, security, and verifiability.
How Blockchain Helps:
- Secure & Transparent Voting: Each vote can be recorded as an immutable transaction on the blockchain, making it auditable and virtually impossible to alter. This could increase public trust in election results.
- Enhanced Voter Verification: Blockchain can securely verify voter eligibility without compromising privacy.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): Blockchain powers DAOs, which are organizations governed by rules encoded as smart contracts. Members vote on proposals, and decisions are automatically executed, creating transparent and community-driven governance models.
6. Intellectual Property (IP) & Royalties
Artists, musicians, writers, and inventors often struggle with proving ownership and fairly distributing royalties. Blockchain offers a powerful solution.
How Blockchain Helps:
- Proof of Ownership: Creators can timestamp their original work on the blockchain, providing an immutable record of creation and ownership. This makes it easier to protect copyrights and patents.
- Automated Royalty Distribution: Smart contracts can automatically distribute royalties to artists, co-creators, and rights holders every time their work is used or sold, ensuring fair and immediate payment without intermediaries.
- Licensing & Usage Tracking: Blockchain can track how intellectual property is licensed and used, providing transparency and ensuring compliance with agreements.
7. Energy & Utilities
From managing energy grids to facilitating peer-to-peer energy trading, blockchain can bring efficiency and transparency to the energy sector.
How Blockchain Helps:
- Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading: Homeowners with solar panels can sell their excess energy directly to neighbors using blockchain-powered platforms, bypassing traditional utility companies and fostering local energy markets.
- Grid Management: Blockchain can help manage and balance energy supply and demand in decentralized grids, particularly with the rise of renewable energy sources.
- Carbon Credit Trading: Creating a transparent and verifiable system for trading carbon credits can incentivize sustainable practices and combat climate change.
8. Gaming & Digital Collectibles (NFTs)
While Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) are a form of cryptocurrency, their application in gaming and digital art goes beyond mere currency. They represent verifiable digital ownership.
How Blockchain Helps:
- True Ownership of In-Game Assets: Players can truly own their in-game items (weapons, skins, characters) as NFTs. These assets can be traded, sold, or even used across different games, creating new economies for gamers.
- Digital Collectibles & Art: NFTs provide a way to verify the authenticity and ownership of unique digital assets, revolutionizing the digital art market.
- Play-to-Earn Models: Blockchain enables games where players can earn cryptocurrencies or NFTs through gameplay, creating new economic opportunities.
9. Financial Services (Beyond Cryptocurrencies)
Even traditional financial institutions are leveraging blockchain for more than just speculative trading.
How Blockchain Helps:
- Cross-Border Payments & Remittances: Blockchain can significantly reduce the time and cost of international money transfers by eliminating intermediaries and enabling near-instantaneous settlements.
- Trade Finance: Streamlining the complex and paper-heavy processes of international trade finance, from letters of credit to invoice financing, using smart contracts for automated execution.
- Asset Tokenization: Representing real-world assets (like stocks, bonds, or commodities) as digital tokens on a blockchain, enabling fractional ownership, increased liquidity, and faster settlement.
- Clearing & Settlement: Reducing the time it takes to settle transactions in capital markets from days to minutes, thereby reducing risk and freeing up capital.
10. Education & Credentials
Verifying educational achievements and professional qualifications can be a cumbersome process. Blockchain offers a secure and efficient alternative.
How Blockchain Helps:
- Verifiable Credentials: Educational institutions can issue degrees, diplomas, and certifications as immutable records on the blockchain. This allows employers to instantly verify qualifications without needing to contact the issuing institution.
- Lifelong Learning Records: Individuals can build a comprehensive and verifiable record of their skills, courses, and professional development throughout their career.
- Combating Diploma Mills: The immutability of blockchain records makes it extremely difficult to forge educational credentials.
The Overarching Benefits of Blockchain Across Industries
As we’ve seen, the specific applications of blockchain are diverse, but they all stem from a common set of powerful benefits:
- Increased Trust: By providing an immutable and transparent record, blockchain fosters trust between parties who may not know each other.
- Enhanced Security: The cryptographic nature of blockchain makes it highly resistant to hacking, fraud, and data tampering.
- Greater Transparency: While privacy can be maintained, the verifiable nature of transactions provides an unprecedented level of accountability.
- Improved Efficiency: Automation through smart contracts and the elimination of intermediaries can drastically reduce processing times and manual effort.
- Reduced Costs: Lowering reliance on third parties, cutting down on paperwork, and streamlining operations can lead to significant cost savings.
- New Business Models: Blockchain enables entirely new ways of doing business, from fractional ownership to decentralized autonomous organizations.
Challenges and the Future Outlook
Despite its immense potential, blockchain technology is still evolving. Challenges remain, including:
- Scalability: Processing a massive volume of transactions efficiently can be a technical hurdle for some blockchain networks.
- Regulatory Clarity: Governments worldwide are still developing frameworks to regulate blockchain and digital assets.
- Interoperability: Different blockchain networks often struggle to communicate with each other.
- Adoption & Education: Widespread adoption requires overcoming inertia, educating users, and integrating blockchain into existing legacy systems.
However, the pace of innovation is rapid. Developers are constantly working on solutions to these challenges, and we are seeing increasing collaboration between enterprises, governments, and blockchain communities. As the technology matures and becomes more accessible, its real-world impact will only grow.
Conclusion: Blockchain is More Than Just a Buzzword
Blockchain is not just a technological fad; it’s a foundational technology with the potential to fundamentally transform how we interact, transact, and share information across virtually every industry. By providing an unparalleled level of security, transparency, and efficiency, it empowers organizations and individuals alike.
From ensuring the authenticity of your food to securing your medical records, verifying your educational achievements, or streamlining global trade, blockchain is quietly building the infrastructure for a more trusted, efficient, and decentralized future. As we look beyond the hype of cryptocurrencies, the true power of blockchain lies in its ability to solve real-world problems and unlock new possibilities for innovation and collaboration. The decentralized revolution is just beginning, and its impact will be felt for generations to come.


Post Comment