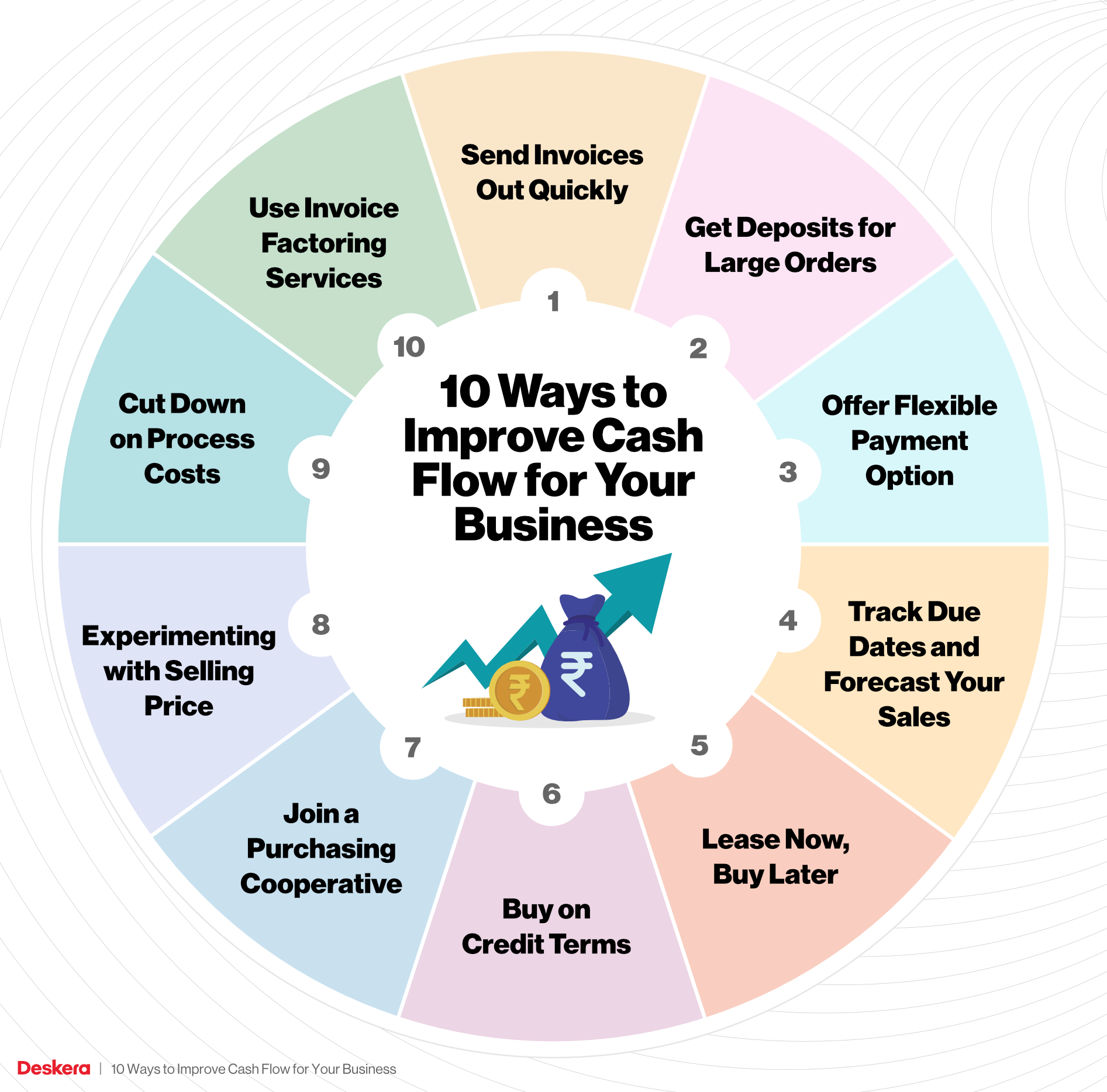
Mastering Inventory Management: Powerful Strategies to Boost Your Cash Flow & Profitability
A Beginner-Friendly Guide to Optimizing Stock and Unleashing Capital
In the world of business, cash is king. It’s the lifeblood that keeps your operations running, allows for investments, and helps you weather economic storms. But for many businesses, especially those dealing with physical products, a significant portion of that precious cash can get tied up – not in a bank account, but in your inventory.
Imagine your warehouse or stockroom not just as a storage facility, but as a bank vault. Every item sitting on those shelves represents money you’ve spent that isn’t currently generating revenue. This is where inventory management comes into play. It’s not just about counting boxes; it’s about strategically controlling the flow of goods to optimize your cash flow, reduce costs, and ultimately, boost your bottom line.
This comprehensive guide will break down the essential inventory management strategies in an easy-to-understand way, helping even beginners transform their stock into a source of financial strength.
Why Your Inventory Management Directly Impacts Your Cash Flow
Before diving into strategies, let’s understand the critical link between your stock and your financial health.
1. Cash Tied Up (Working Capital):
- The Problem: Every dollar you spend acquiring inventory (purchasing raw materials, manufacturing products, shipping finished goods) is a dollar that isn’t available for other critical business needs like marketing, salaries, or new equipment. This is your working capital – the money available for day-to-day operations.
- The Impact: Too much inventory means less working capital, potentially leading to cash flow shortages even if sales are good.
2. Holding Costs (Carrying Costs):
- The Problem: Inventory isn’t free once it arrives. It comes with a host of "holding costs" that eat into your profits.
- Examples of Holding Costs:
- Storage Costs: Rent for warehouse space, utilities, shelving.
- Insurance: Protecting your goods from damage, theft, or natural disasters.
- Obsolescence & Spoilage: Products becoming outdated, damaged, or expiring, making them unsellable.
- Shrinkage: Loss due to theft, damage, or administrative errors.
- Opportunity Cost: The profit you could have made if that money tied up in inventory was invested elsewhere (e.g., in a high-return marketing campaign).
3. Risk of Dead Stock:
- The Problem: This is the ultimate cash drain. "Dead stock" refers to inventory that hasn’t sold for a long time and is unlikely to sell in the future. It’s literally money gathering dust.
- The Impact: Not only does it incur holding costs, but it also takes up valuable space that could be used for profitable items.
By mastering inventory management, you can free up capital, minimize these costs, and ensure your business has the cash it needs to thrive.
Key Inventory Management Strategies to Boost Your Cash Flow
Now, let’s explore actionable strategies you can implement, even if you’re just starting out.
1. Implement Accurate Demand Forecasting
Think of forecasting like predicting the weather for your products. You want to know how much customers will want and when, so you can have just enough without having too much or too little.
- How it Boosts Cash Flow:
- Prevents Overstocking: Avoids tying up excessive cash in goods that sit idle.
- Minimizes Stockouts: Ensures you have products when customers want them, preventing lost sales and frustrated customers.
- How to Do It (Beginner-Friendly):
- Analyze Historical Sales Data: Look at past sales trends – weekly, monthly, quarterly. Identify peaks and valleys.
- Consider Seasonality: Do your sales spike during holidays, specific seasons (e.g., summer, back-to-school), or special events?
- Factor in Promotions & Marketing: If you’re planning a sale or a big marketing push, expect increased demand.
- Monitor Market Trends: Are new competitors emerging? Is a new product about to make yours obsolete? Stay informed.
- Talk to Your Sales Team: They’re on the front lines and often have invaluable insights into customer needs and upcoming trends.
2. Adopt Smart Inventory Control Methods
Not all inventory is created equal. Some items sell quickly and are vital; others are slow-movers but might be crucial components. Different methods help you manage them effectively.
-
A. ABC Analysis:
- Concept: Categorize your inventory based on its value or importance to your business. This helps you focus your efforts where they matter most.
- Categories:
- "A" Items (High Value, Low Volume): These are your most important items, representing a large percentage of your total inventory value but a small percentage of your total stock count. (e.g., a high-end designer bag, a critical machine part).
- Strategy: Tightly control these. Monitor them frequently, forecast precisely, and ensure security.
- "B" Items (Medium Value, Medium Volume): These are moderately important.
- Strategy: Regular monitoring, less stringent than "A" items.
- "C" Items (Low Value, High Volume): These are numerous but represent a small portion of your total inventory value. (e.g., pens, screws, basic t-shirts).
- Strategy: Can be managed with simpler, less frequent checks. You might keep larger quantities on hand to avoid constant reordering.
- "A" Items (High Value, Low Volume): These are your most important items, representing a large percentage of your total inventory value but a small percentage of your total stock count. (e.g., a high-end designer bag, a critical machine part).
- How it Boosts Cash Flow: By focusing tight control on high-value items, you minimize the risk of losses where it hurts most, freeing up time and resources for other areas.
-
B. Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory:
- Concept: Receive goods from suppliers only as you need them for production or sale, rather than holding large stocks. Think of it like a restaurant ordering fresh ingredients daily rather than buying a month’s supply.
- How it Boosts Cash Flow:
- Drastically reduces holding costs (storage, insurance).
- Minimizes the risk of obsolescence or spoilage.
- Frees up a lot of capital that would otherwise be tied up in warehouses.
- Considerations: Requires extremely reliable suppliers and efficient logistics. Any delay can halt operations. Best suited for businesses with predictable demand and strong supplier relationships.
3. Leverage Technology: Inventory Management Software
Gone are the days of manual spreadsheets and clipboards. Modern inventory management software is a game-changer for cash flow.
- How it Boosts Cash Flow:
- Real-time Visibility: Know exactly what you have, where it is, and its status at any given moment. This prevents unnecessary purchases.
- Automated Tracking: Reduces human error, saving time and preventing costly mistakes.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Software can analyze sales trends, forecast demand, and suggest optimal reorder points.
- Integration: Many systems integrate with your sales (POS), accounting, and e-commerce platforms, providing a holistic view of your business.
- For Beginners: Start with cloud-based, user-friendly options designed for small to medium-sized businesses. Many offer free trials or affordable monthly subscriptions. Look for features like barcode scanning, multi-location tracking (if applicable), and reporting.
4. Optimize Reorder Points and Safety Stock
This strategy is about finding the "Goldilocks zone" – not too much, not too little.
- Reorder Point:
- Concept: The specific level of inventory at which you should place a new order to replenish stock. It’s calculated based on your lead time (how long it takes for a new order to arrive) and your average daily sales.
- Example: If you sell 10 units a day and it takes 5 days for a new order to arrive, your reorder point might be 50 units (10 units/day * 5 days).
- Safety Stock:
- Concept: A small buffer of extra inventory kept on hand to prevent stockouts due to unexpected demand spikes or supplier delays.
- How it Boosts Cash Flow: Prevents lost sales from stockouts without holding excessive inventory. It’s an insurance policy, not a regular reserve.
- The Balance: By setting intelligent reorder points and maintaining a calculated safety stock, you minimize both the risk of running out of popular items (losing sales) and the cost of holding too much inventory (tying up cash).
5. Cultivate Strong Supplier Relationships
Your suppliers are partners in your inventory management journey. Good relationships can directly impact your cash flow.
- How it Boosts Cash Flow:
- Better Pricing: Long-term relationships can lead to volume discounts or preferential pricing.
- Flexible Payment Terms: Negotiate longer payment terms (e.g., Net 30, Net 60), allowing you to sell products and collect cash before you have to pay your supplier. This is a direct boost to your working capital.
- Faster & More Reliable Deliveries: Crucial for JIT strategies and reducing the need for large safety stock.
- Returns Policy: Understand and leverage their return policies for defective or slow-moving items.
- Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI): In some cases, suppliers might take responsibility for managing your inventory levels, replenishing stock automatically. This frees up your time and resources.
6. Strategically Deal with Dead Stock and Obsolescence
Don’t let dead stock linger. It’s a constant drain on your cash flow.
- How it Boosts Cash Flow: Frees up capital, storage space, and reduces ongoing holding costs.
- Actions to Take:
- Identify Early: Regularly review inventory aging reports to spot slow-moving items before they become truly "dead."
- Aggressive Discounts: A smaller profit (or even a slight loss) is better than a total loss. Offer flash sales, percentage off, or buy-one-get-one-free deals.
- Bundling: Pair slow-moving items with popular products at a discounted combined price.
- Liquidation: Sell to an outlet, a liquidator, or even an online auction site specializing in excess inventory.
- Donation: If it’s unsellable, donating can offer tax benefits and goodwill.
- Return to Supplier: Check your supplier agreements for return clauses.
7. Conduct Regular Inventory Audits and Cycle Counts
Accuracy is paramount. You can’t manage what you don’t accurately know you have.
- How it Boosts Cash Flow:
- Prevents Discrepancies: Ensures your physical count matches your records, avoiding costly misjudgments in purchasing.
- Identifies Theft/Damage Early: Allows you to address issues before they become major losses.
- Improves Data Reliability: Accurate data leads to better forecasting and purchasing decisions.
- Methods:
- Physical Inventory: A complete count of all items, usually done once a year. It’s disruptive but provides a full snapshot.
- Cycle Counting: Counting a small, specific section of your inventory on a regular, rotating basis. This is less disruptive and helps maintain continuous accuracy without shutting down operations.
8. Monitor Key Inventory Performance Indicators (KPIs)
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. KPIs provide insights into the health of your inventory and its impact on cash flow.
- Key KPIs to Track:
- Inventory Turnover Ratio:
- Formula: Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory
- What it Means: How many times your entire inventory has been sold and replaced over a period (e.g., a year). A higher ratio generally indicates efficient inventory management and better cash flow.
- Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO) / Days Sales of Inventory (DSI):
- Formula: (Average Inventory / Cost of Goods Sold) * 365
- What it Means: The average number of days it takes for your inventory to be converted into sales. A lower number is better, indicating less cash tied up.
- Stockout Rate:
- What it Means: The percentage of customer orders you couldn’t fulfill due to lack of stock. A high rate means lost sales and unhappy customers.
- Holding Costs as a Percentage of Inventory Value:
- What it Means: Helps you understand the true cost of keeping inventory.
- Inventory Turnover Ratio:
The Benefits of Optimized Inventory Management
Implementing these strategies isn’t just about spreadsheets and stockrooms; it translates directly into tangible business advantages:
- Increased Cash Flow: The most direct benefit – more money available for operations, investments, or simply building a stronger financial reserve.
- Reduced Operating Costs: Lower holding costs, less waste from obsolescence, and fewer expedited shipping fees.
- Improved Profitability: By cutting costs and avoiding lost sales, your profit margins naturally improve.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Fewer stockouts mean customers get what they want, when they want it, leading to loyalty and positive reviews.
- Better Business Decision-Making: Accurate data empowers you to make informed choices about purchasing, pricing, and expansion.
- Greater Business Agility: With less cash tied up, you’re more flexible to respond to market changes, new opportunities, or unexpected challenges.
Getting Started: Your Action Plan for Beginners
Feeling overwhelmed? Don’t be. Start small and build momentum.
- Assess Your Current Situation: What’s your biggest inventory pain point right now? Too much dead stock? Frequent stockouts? No idea what you even have?
- Set Clear Goals: Do you want to reduce holding costs by 10%? Improve inventory turnover by 20%?
- Choose One or Two Strategies to Start: Don’t try to implement everything at once. Maybe begin with improving your forecasting or implementing ABC analysis.
- Consider Basic Software: Even a simple, affordable inventory tracking tool can make a huge difference in accuracy and visibility.
- Train Your Team: Ensure everyone involved in inventory (purchasing, sales, warehouse staff) understands the new processes and their importance.
- Start Small, Learn, and Iterate: Implement changes, monitor the results, and adjust your approach as you learn what works best for your specific business.
Conclusion: Your Inventory, Your Cash Flow Powerhouse
Inventory management might sound like a dry, back-office task, but its impact on your business’s financial health is profound. By moving beyond reactive stock control to proactive, strategic inventory management, you transform your stock from a cash sinkhole into a powerful engine for boosting cash flow and profitability.
Embrace these strategies, leverage technology, and cultivate strong relationships, and you’ll soon find your business operating more efficiently, with healthier cash reserves and a stronger foundation for sustainable growth. Start today – your cash flow will thank you!



Post Comment