Unmasking Cybersecurity Threats: A Comprehensive Guide to Protecting Your Business from Modern Cyber Attacks
In today’s hyper-connected world, every business, regardless of size, operates in a digital landscape. While this offers unprecedented opportunities for growth and efficiency, it also opens the door to a growing number of cybersecurity threats. From a small local bakery managing online orders to a multinational corporation handling vast amounts of sensitive data, the risk of a cyber attack is no longer a question of "if," but "when."
Ignoring cybersecurity is like leaving your business’s front door wide open in a bustling city. The consequences of a data breach, ransomware attack, or other cyber incidents can be devastating, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, legal penalties, and even business closure.
This comprehensive guide is designed to help business owners and managers, even those new to the world of technology, understand the most common cybersecurity threats and, more importantly, how to build robust defenses to protect your business from attacks.
Why Cybersecurity is No Longer Optional for Any Business
Gone are the days when cybersecurity was solely the concern of large tech companies. Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are increasingly targeted because they often have fewer resources dedicated to security, making them easier prey. Here’s why robust cybersecurity is absolutely crucial for your business:
- Financial Loss: Cyber attacks can be incredibly expensive. This includes the cost of recovering data, repairing systems, notifying affected customers, legal fees, and regulatory fines. Ransomware demands can also directly drain your funds.
- Reputational Damage: A data breach erodes customer trust. If customers feel their personal information isn’t safe with you, they’ll take their business elsewhere. Rebuilding a damaged reputation can take years, if it’s possible at all.
- Operational Disruption: Attacks can shut down your operations, preventing you from serving customers, processing orders, or even accessing your own files. This downtime directly translates to lost revenue and productivity.
- Loss of Sensitive Data: This could include customer credit card details, employee personal information, proprietary business secrets, or intellectual property. Such losses can have long-lasting consequences.
- Legal & Regulatory Penalties: Depending on your industry and location (e.g., GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA), data breaches can result in hefty fines and legal action from regulators and affected individuals.
- Business Closure: For some businesses, particularly SMBs, the financial and reputational fallout from a major cyber attack can be so severe that it forces them to close their doors permanently.
Understanding the Enemy: Common Cybersecurity Threats Your Business Faces
To protect your business effectively, you need to know what you’re up against. Cyber attackers use various methods to gain unauthorized access, steal data, or disrupt operations. Here are some of the most prevalent cybersecurity threats:
1. Phishing & Social Engineering
- What it is: This is perhaps the most common starting point for many cyber attacks. Phishing involves tricking individuals into revealing sensitive information (like passwords or credit card numbers) or clicking on malicious links. Social engineering broadly refers to manipulating people into performing actions or divulging confidential information.
- How it works: Attackers send fake emails, text messages, or even make phone calls disguised as legitimate sources (e.g., your bank, a known vendor, a colleague, or even the CEO). They often create a sense of urgency or fear to make you act without thinking.
- Example: An email appearing to be from your bank asks you to "verify your account details" by clicking a link, which then takes you to a fake website designed to steal your login credentials.
2. Ransomware Attacks
- What it is: Ransomware is a type of malicious software (malware) that encrypts your files, making them inaccessible. The attackers then demand a ransom (usually in cryptocurrency) in exchange for a decryption key to unlock your data.
- How it works: It often spreads through phishing emails, malicious websites, or vulnerable software. Once inside your network, it quickly encrypts critical files and displays a ransom note.
- Impact: Can bring your entire business to a halt, leading to massive data loss if you don’t pay or have proper backups. Even paying the ransom doesn’t guarantee your data will be recovered.
3. Malware (Viruses, Spyware, Worms, Trojans)
- What it is: An umbrella term for various types of malicious software designed to disrupt computer operations, gather sensitive information, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems.
- Viruses: Attach to legitimate programs and spread when those programs are executed.
- Spyware: Secretly monitors your computer activity and collects personal information.
- Worms: Self-replicating malware that spreads across networks without human intervention.
- Trojans: Disguise themselves as legitimate software but carry malicious payloads.
- How it works: Often delivered through email attachments, infected websites, or compromised software downloads.
- Impact: Can lead to data corruption, system slowdowns, theft of information, and provide a backdoor for further attacks.
4. Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
- What it is: A DDoS attack attempts to overwhelm a server, service, or network with a flood of internet traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users.
- How it works: Attackers use a network of compromised computers (a "botnet") to simultaneously send massive amounts of traffic to a target, effectively shutting it down.
- Impact: Can lead to significant downtime for your website, online services, or internal network, disrupting business operations and costing you sales.
5. Insider Threats
- What it is: This refers to security risks that originate from within your own organization. This can be an employee, former employee, contractor, or business partner who has access to your systems and data.
- How it works:
- Malicious Insiders: Individuals intentionally steal data, sabotage systems, or leak confidential information.
- Negligent Insiders: Employees accidentally cause a breach through carelessness, such as falling for a phishing scam, losing a company device, or misconfiguring a system.
- Impact: Can be difficult to detect and often leads to significant data loss or system damage, sometimes with long-lasting consequences due to the trust factor.
6. Password Attacks
- What it is: Attempts by attackers to gain unauthorized access to accounts by guessing or cracking passwords.
- How it works:
- Brute Force: Trying every possible combination of characters until the correct password is found.
- Dictionary Attacks: Using common words, phrases, and password patterns.
- Credential Stuffing: Using stolen username/password combinations from one breach to try logging into other services, hoping users reuse passwords.
- Impact: If successful, attackers gain direct access to sensitive systems and data.
Signs Your Business Might Be Under Attack
Early detection is key to minimizing damage. While some attacks are stealthy, others leave clues. Train yourself and your employees to recognize these warning signs:
- Unusual Network Activity: Sudden spikes in outgoing data, unrecognized connections, or strange network traffic patterns.
- Locked Accounts: Employees suddenly find their accounts locked out, indicating multiple failed login attempts.
- Missing or Altered Files: Files are suddenly gone, encrypted, or have been modified without your knowledge.
- Slow System Performance: Computers or your network are unusually slow, often a sign that malware is running in the background.
- Unexpected Pop-ups or Messages: Unusual error messages, new toolbars in browsers, or strange pop-up ads, especially those demanding money.
- Changes to System Settings: Unauthorized changes to your computer’s security settings, homepage, or other configurations.
- Customer Complaints: Customers report receiving spam emails from your domain, or complain about suspicious activity related to their accounts with your business.
- Antivirus Alerts: Your antivirus software is frequently detecting threats or has been disabled without your permission.
Protecting Your Business: Actionable Steps to Build Your Cyber Defenses
Building a strong cybersecurity posture doesn’t happen overnight, but it’s an ongoing process that is vital for survival in the digital age. Here are the essential steps your business should take:
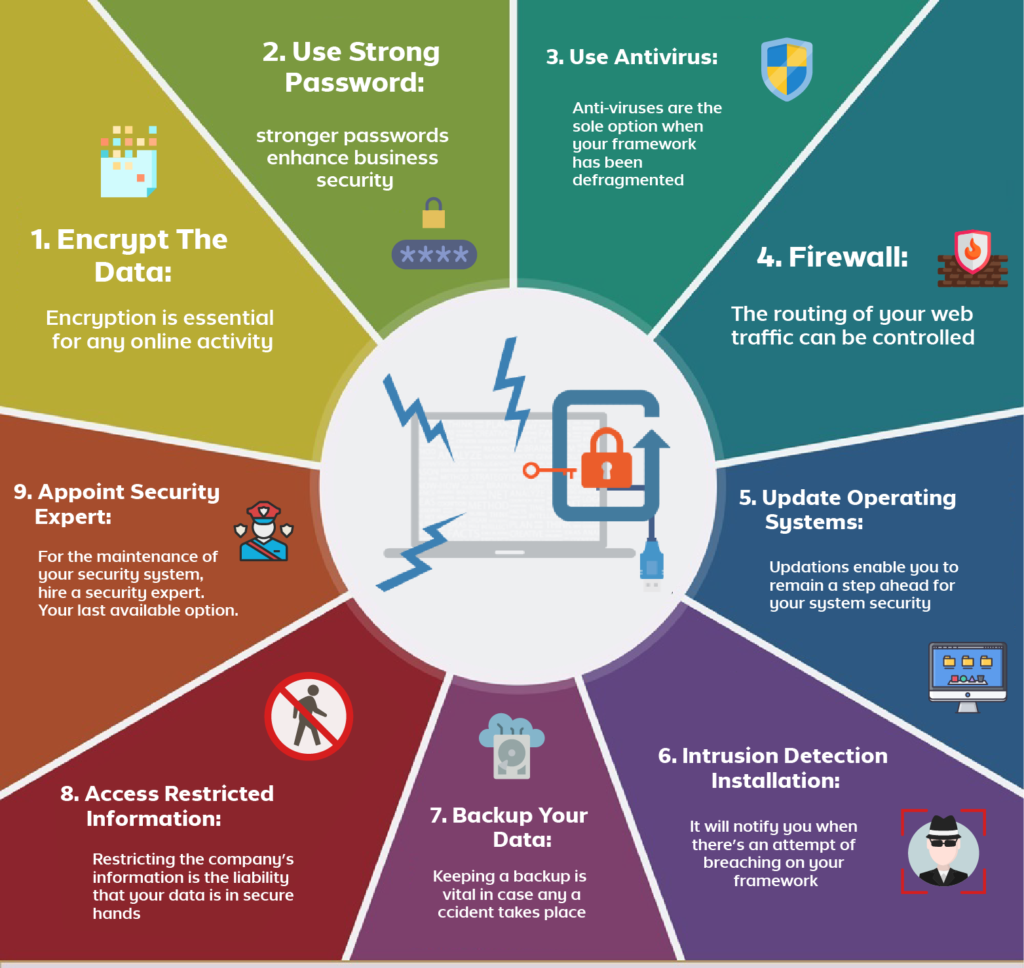
1. Implement Strong Password Policies & Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Action: Enforce the use of long, complex, and unique passwords for all accounts. Crucially, enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) wherever possible (email, banking, cloud services, internal systems).
- Why it helps: MFA adds an extra layer of security beyond just a password (e.g., a code sent to your phone). Even if an attacker steals a password, they can’t access the account without the second factor. This is one of the most effective defenses against stolen credentials.
2. Keep All Software and Systems Updated
- Action: Regularly update operating systems (Windows, macOS), web browsers, antivirus software, and all business applications. Enable automatic updates where possible.
- Why it helps: Software updates often include "patches" for security vulnerabilities that attackers exploit. Outdated software is a common entry point for malware and other attacks.
3. Deploy Robust Firewalls and Antivirus/Anti-Malware Solutions
- Action: Install and maintain a reputable antivirus/anti-malware program on all computers and servers. Ensure your network has a strong firewall that monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic.
- Why it helps: Firewalls act as a barrier between your internal network and the internet, blocking unauthorized access. Antivirus software detects and removes known threats.
4. Back Up Your Data Regularly and Securely
- Action: Implement a routine schedule for backing up all critical business data. Store backups in a separate, secure location (off-site or in the cloud) and test them regularly to ensure they can be restored.
- Why it helps: This is your last line of defense against data loss due to ransomware, accidental deletion, or system failure. If your primary data is compromised, you can restore from a clean backup.
5. Educate Your Employees: The Human Firewall
- Action: Conduct regular cybersecurity awareness training for all employees. Teach them how to recognize phishing emails, report suspicious activity, create strong passwords, and understand company security policies.
- Why it helps: Employees are often the weakest link in a company’s security. A well-trained workforce becomes your first and most effective line of defense against social engineering and phishing attacks.
6. Implement Access Control and Principle of Least Privilege
- Action: Limit employee access to only the data and systems they need to perform their job functions. Regularly review and update access permissions, especially when employees change roles or leave the company.
- Why it helps: Minimizes the potential damage if an employee’s account is compromised or if an insider threat emerges. If an attacker gains access to one account, they can’t automatically access everything.
7. Secure Your Wi-Fi Network
- Action: Use strong encryption (WPA2 or WPA3) for your business Wi-Fi. Change default router passwords, and consider setting up a separate guest Wi-Fi network for visitors.
- Why it helps: An unsecured Wi-Fi network is an open invitation for attackers to access your internal network.
8. Develop an Incident Response Plan
- Action: Create a clear, step-by-step plan for what to do in the event of a cyber attack. This should include who to notify, how to isolate affected systems, data recovery procedures, and communication strategies.
- Why it helps: A well-rehearsed plan minimizes panic, reduces recovery time, and limits the damage during a crisis. It ensures you can respond effectively and efficiently.
9. Conduct Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
- Action: Periodically hire cybersecurity professionals to conduct security audits and penetration tests. An audit identifies vulnerabilities, while penetration testing simulates a real-world attack to find weaknesses.
- Why it helps: Proactively identifies weaknesses in your defenses before malicious attackers can exploit them. It provides an objective assessment of your security posture.
10. Consider Cybersecurity Insurance
- Action: Explore obtaining a dedicated cybersecurity insurance policy.
- Why it helps: While not a prevention tool, it can help cover the financial costs associated with a data breach, such as legal fees, notification costs, forensics, and business interruption.
Building a Cybersecurity Culture: It’s Everyone’s Responsibility
Cybersecurity isn’t just an IT department’s job; it needs to be integrated into your company’s DNA.
- Lead by Example: Business owners and senior management must champion cybersecurity best practices. If leadership takes it seriously, employees are more likely to follow suit.
- Make it Simple: Avoid overly technical jargon in training. Explain the "why" behind policies in a way that resonates with everyone.
- Encourage Reporting: Create an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting suspicious emails or activity without fear of blame. This allows for quick action before small issues become big problems.
- Continuous Learning: The threat landscape is always evolving. Regularly update your security policies and provide ongoing training to keep employees informed about new threats and best practices.
Conclusion: Your Business’s Digital Shield
The digital world offers immense opportunities, but it also presents significant risks. Cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving, becoming more sophisticated and targeting businesses of all sizes. By understanding these threats and proactively implementing the protective measures outlined in this guide, you are not just investing in technology; you are investing in the very survival and success of your business.
Don’t wait for an attack to happen. Start building your business’s digital shield today. Your data, your reputation, and your future depend on it.



Post Comment