
Unlocking Business Potential: A Beginner’s Guide to the Internet of Things (IoT) in Business
Imagine a world where your machinery tells you it needs maintenance before it breaks down, where your inventory manages itself, and where your customers receive hyper-personalized experiences without you lifting a finger. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the power of the Internet of Things (IoT) in action, revolutionizing how businesses operate, innovate, and connect with their world.
For many, "Internet of Things" sounds complex or futuristic. But at its core, IoT is simply about connecting everyday objects to the internet, allowing them to send and receive data. When applied to business, this concept transforms into a powerful engine for efficiency, insight, and competitive advantage.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll demystify IoT for business, breaking down what it is, why it matters, how it’s being used today, and what you need to consider to leverage its incredible potential.
What Exactly is the Internet of Things (IoT)? A Simple Explanation
Think of the regular internet as connecting people (via computers, phones). The Internet of Things extends this idea to things. It’s a vast network of physical objects – from tiny sensors to complex machines – embedded with electronics, software, sensors, actuators, and network connectivity that allows them to collect and exchange data.
In simpler terms, IoT means:
- Things that Talk: Devices that can communicate with each other and with central systems over the internet.
- Data Collection: These "things" gather information about their environment, status, or usage.
- Smart Actions: Based on this data, they can trigger actions, automate processes, or provide valuable insights.
Key Components of an IoT System:
- Things (Devices/Sensors): These are the physical objects equipped with sensors to collect data (e.g., temperature, pressure, location) or actuators to perform actions (e.g., open a valve, adjust a thermostat).
- Connectivity: This is how the "things" send their data to the internet. It can be Wi-Fi, cellular (4G/5G), Bluetooth, LoRaWAN, or other specialized networks.
- Data Processing: Once the data is collected, it’s sent to a central cloud platform or a local server (edge computing) for processing and analysis.
- User Interface/Applications: This is where you, the business user, see the data, analyze insights, and control the IoT devices through dashboards, mobile apps, or other software.
Why IoT Matters for Your Business: The Core Benefits
The adoption of IoT isn’t just a trend; it’s a strategic imperative for businesses looking to stay competitive and drive growth. Here’s why IoT is becoming indispensable:
-
Operational Efficiency & Cost Savings:
- Automation: IoT devices can automate repetitive tasks, reducing the need for manual intervention and freeing up human resources for more complex work.
- Resource Optimization: Monitoring energy consumption, water usage, or raw materials allows businesses to identify waste and optimize resource allocation.
- Reduced Downtime: Predictive maintenance (explained below) significantly cuts down on unexpected equipment failures and costly downtime.
-
Enhanced Customer Experience:
- Personalization: Understanding customer behavior through connected products can lead to highly personalized services, offers, and support.
- Improved Service: Remote monitoring of products in the field allows for proactive troubleshooting and quicker resolution of issues.
- New Offerings: IoT enables "product-as-a-service" models, where businesses sell the outcome or usage of a product rather than just the product itself.
-
New Revenue Streams & Business Models:
- IoT can unlock entirely new ways to generate income. For example, a company that traditionally sold industrial machinery might now offer "machine uptime" as a service, charging based on how much time the machine is operational.
- Data collected from IoT devices can be anonymized and aggregated to create valuable market insights that can be sold or used to develop new products.
-
Data-Driven Decision Making:
- IoT generates a massive amount of real-time data. This data, when properly analyzed, provides unparalleled insights into operations, customer behavior, asset performance, and market trends.
- Businesses can move from reactive problem-solving to proactive, informed strategic planning.
-
Predictive Maintenance:
- Instead of waiting for equipment to break down (reactive) or performing maintenance on a fixed schedule (preventive), IoT sensors can monitor the condition of machinery in real-time.
- They can detect early signs of wear and tear, unusual vibrations, or temperature spikes, allowing maintenance to be scheduled before a failure occurs, saving significant costs and preventing production halts.
-
Supply Chain Optimization:
- Tracking goods in transit, monitoring storage conditions (temperature, humidity), and managing inventory levels in real-time.
- This leads to reduced spoilage, improved delivery times, and more efficient warehousing.
-
Improved Safety & Compliance:
- Monitoring environmental conditions in hazardous areas, tracking worker location, or ensuring equipment operates within safety parameters.
- IoT can help businesses meet regulatory requirements and create safer working environments.
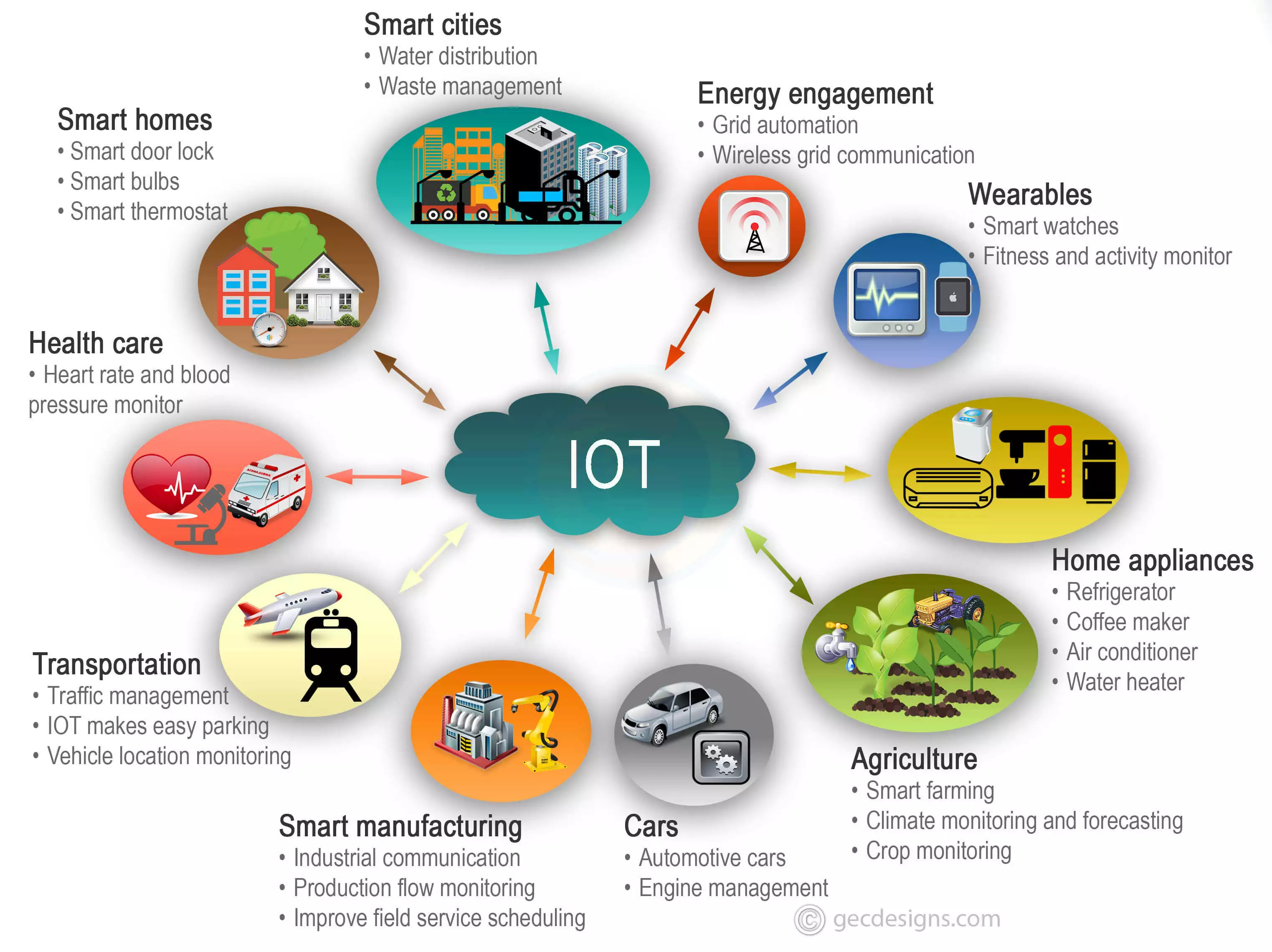
Real-World IoT Applications in Business: Industry Examples
IoT isn’t just a concept; it’s actively transforming various industries. Here are a few prominent examples:
-
Manufacturing (Industry 4.0 / Smart Factories):
- Asset Tracking: Knowing the exact location of tools, parts, and finished products on the factory floor.
- Quality Control: Sensors monitoring production lines to detect defects in real-time, reducing waste.
- Predictive Maintenance: As mentioned, preventing costly machinery breakdowns.
- Remote Monitoring: Overseeing entire production processes from a central control room, even off-site.
-
Retail:
- Smart Shelves: Sensors that detect when inventory is low and automatically reorder, or track customer interaction with products.
- Personalized Marketing: Beacons in stores that send personalized offers to customers’ phones based on their location and preferences.
- Optimized Store Layouts: Analyzing foot traffic patterns to improve store navigation and product placement.
-
Healthcare (Connected Health):
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Wearable devices and in-home sensors tracking vital signs, glucose levels, or activity, allowing doctors to monitor patients remotely and intervene proactively.
- Smart Hospitals: Asset tracking for medical equipment, intelligent climate control, and patient flow optimization.
- Medication Adherence: Smart pill dispensers that remind patients to take medication and track dosage.
-
Logistics & Transportation:
- Fleet Management: GPS tracking of vehicles, monitoring driver behavior, fuel consumption, and vehicle diagnostics.
- Cold Chain Monitoring: Sensors in refrigerated trucks and containers ensuring temperature-sensitive goods (food, pharmaceuticals) remain at optimal conditions.
- Route Optimization: Real-time traffic and weather data informing the most efficient delivery routes.
-
Agriculture (Smart Farming):
- Precision Agriculture: Sensors monitoring soil moisture, nutrient levels, and weather conditions to optimize irrigation and fertilization.
- Livestock Monitoring: Wearable sensors on animals to track health, location, and breeding cycles.
- Automated Irrigation: Systems that turn on sprinklers only when needed, conserving water.
-
Smart Buildings & Offices:
- Energy Management: IoT sensors adjusting lighting, heating, and cooling based on occupancy and external conditions to save energy.
- Space Utilization: Tracking how office spaces are used to optimize layouts and reduce wasted space.
- Predictive Maintenance for HVAC: Monitoring building systems to prevent failures and ensure comfort.
Key Considerations for IoT Adoption in Your Business
While the benefits are clear, implementing IoT isn’t without its challenges. Understanding these considerations upfront can help you plan for a successful deployment:
-
Security & Privacy:
- Vulnerability: Every connected device is a potential entry point for cyberattacks. Securing the entire IoT ecosystem is paramount.
- Data Privacy: Handling sensitive data collected by IoT devices requires strict adherence to privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
-
Data Management & Analytics:
- Volume: IoT generates vast amounts of data (Big Data). Businesses need robust systems to store, process, and analyze this data effectively.
- Insights: Raw data isn’t useful; extracting meaningful insights requires advanced analytics tools and expertise.
-
Integration Challenges:
- IoT solutions often need to integrate with existing IT systems (ERP, CRM, supply chain management). This can be complex and require significant planning.
- Ensuring interoperability between different devices and platforms can also be a hurdle.
-
Cost of Implementation & Scalability:
- Initial setup costs for sensors, connectivity, platforms, and integration can be significant.
- Businesses need to plan for scalability as their IoT needs grow, ensuring the infrastructure can handle increased data and devices.
-
Skills Gap:
- Implementing and managing IoT solutions requires a diverse set of skills, including hardware, software, networking, data science, and cybersecurity.
- Finding and retaining talent with these specialized skills can be a challenge.
Getting Started with IoT in Your Business: Actionable Steps
Feeling overwhelmed? Don’t be. You don’t have to overhaul your entire business overnight. Here’s a practical approach to begin your IoT journey:
-
Define Clear Goals & Identify Pain Points:
- Don’t just implement IoT for the sake of it. What specific business problem are you trying to solve? (e.g., reduce machinery downtime, improve customer satisfaction, cut energy costs).
- Start with a clear, measurable objective.
-
Start Small with Pilot Projects:
- Choose a single, well-defined use case that offers a clear return on investment (ROI).
- Implement a small-scale pilot project to test the technology, gather data, and understand the challenges. This minimizes risk and allows for learning.
-
Choose the Right Partners:
- Unless you have in-house IoT expertise, consider partnering with experienced IoT solution providers.
- Look for partners who understand your industry, offer end-to-end solutions, and prioritize security.
-
Prioritize Security from Day One:
- Build security into your IoT strategy from the very beginning. Don’t treat it as an afterthought.
- This includes device security, network security, data encryption, and access control.
-
Focus on Data Insights, Not Just Data Collection:
- Remember, the value of IoT lies in the insights you gain from the data, not just the data itself.
- Invest in analytics capabilities and ensure you have the right people to interpret the data and translate it into actionable strategies.
The Future of IoT in Business: What’s Next?
The IoT landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends shaping its future:
- AI & Machine Learning Integration: IoT will increasingly combine with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to make sense of vast datasets, enable more sophisticated predictive analytics, and drive autonomous decision-making.
- Edge Computing: Processing data closer to where it’s collected (at the "edge" of the network) rather than sending everything to the cloud. This reduces latency, saves bandwidth, and enhances real-time responsiveness, crucial for critical applications.
- 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks will provide faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity, enabling more complex and reliable IoT deployments, especially for mission-critical applications.
- Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of physical assets, processes, or systems. IoT data feeds these digital twins, allowing businesses to simulate scenarios, predict performance, and optimize operations in a virtual environment before making changes in the real world.
- Sustainability & Green IoT: IoT will play a crucial role in helping businesses achieve sustainability goals by optimizing energy usage, managing waste, and monitoring environmental conditions.
Conclusion: Embrace the Connected Future
The Internet of Things is more than just a buzzword; it’s a fundamental shift in how businesses can operate, innovate, and thrive in the digital age. By connecting physical assets and extracting actionable insights from their data, businesses can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, deliver superior customer experiences, and unlock entirely new avenues for growth.
While the journey to full IoT adoption may seem daunting, starting small, focusing on clear objectives, and prioritizing security will pave the way for a successful digital transformation. The connected future is here, and businesses that embrace the power of IoT will undoubtedly be the ones that lead the way.
Ready to explore how the Internet of Things can revolutionize your business? Contact an IoT solutions provider today to discuss your unique challenges and opportunities. The future of your business is connected!


Post Comment