Unlocking Efficiency: How AI Transforms Supply Chain Optimization for Smarter Demand & Logistics
The modern global supply chain is a marvel of interconnectedness, but also a complex web prone to disruptions. From unpredictable demand surges to sudden logistical hurdles, businesses often find themselves scrambling to keep up. Empty shelves, delayed deliveries, and excessive waste are common symptoms of an inefficient supply chain. But what if there was a "digital brain" that could anticipate these challenges and guide decisions with incredible accuracy?
Enter Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI is no longer just a futuristic concept; it’s a powerful tool revolutionizing how companies manage their goods, from the factory floor to the customer’s doorstep. This article will explore how AI is becoming the backbone of supply chain optimization, specifically focusing on its incredible ability to predict demand and streamline logistics, making supply chains smarter, faster, and more resilient.
What is AI in Supply Chain Optimization?
At its simplest, Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. This includes learning from data, recognizing patterns, making decisions, and solving problems.
When applied to the Supply Chain, AI acts like a super-smart digital assistant, constantly analyzing vast amounts of information to find the best ways to move products. Instead of relying on guesswork or outdated data, AI provides real-time insights and predictions, helping businesses make informed choices faster.
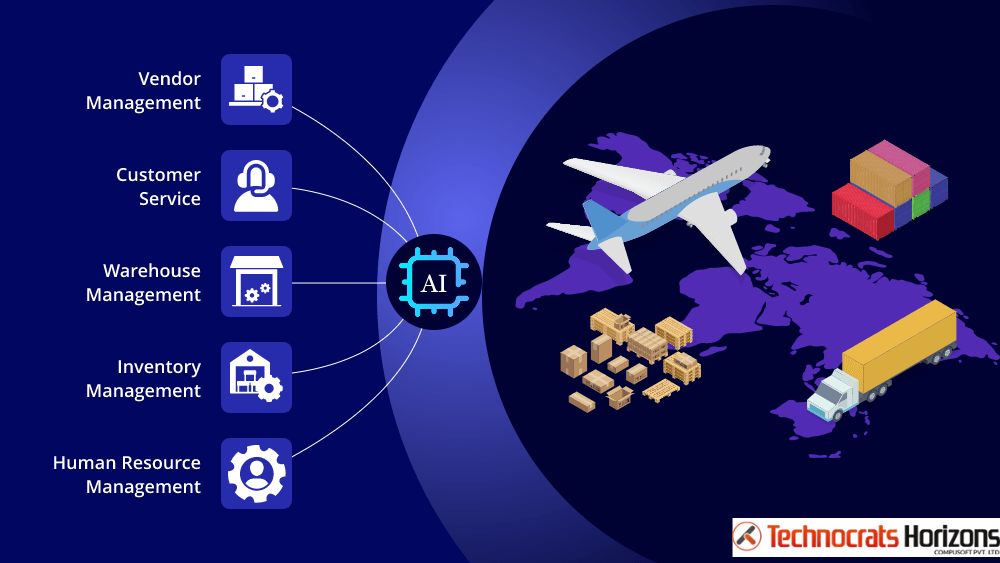
Supply Chain Optimization means making every part of the process as efficient and effective as possible. This includes everything from sourcing raw materials, manufacturing, warehousing, transportation, and delivery to the end customer. AI helps achieve this by:
- Identifying patterns: Spotting trends that humans might miss.
- Predicting outcomes: Forecasting future events with high accuracy.
- Automating decisions: Taking action based on data without human intervention (in some cases).
- Recommending actions: Suggesting the best course of action for complex problems.
Why is AI a Game-Changer for Supply Chains?
Traditional supply chain management often relies on historical data and human intuition, which can be slow and prone to error in today’s fast-changing world. AI, however, brings a new level of precision and agility:
- Reduced Costs:
- Minimizes wasted inventory (less overstocking).
- Optimizes shipping routes (less fuel, fewer delays).
- Reduces labor costs through automation of routine tasks.
- Improved Efficiency & Speed:
- Automates data analysis and decision-making.
- Speeds up order fulfillment and delivery times.
- Streamlines warehouse operations.
- Enhanced Resilience & Risk Management:
- Identifies potential disruptions (e.g., weather events, port closures) in advance.
- Suggests alternative routes or suppliers quickly.
- Helps build more flexible and robust supply networks.
- Better Customer Satisfaction:
- Ensures products are available when customers want them.
- Provides accurate delivery estimates.
- Leads to fewer stockouts and faster service.
- Greater Transparency & Visibility:
- Provides a clearer, real-time view of the entire supply chain.
- Helps track goods at every stage.
- Pinpoints bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
AI’s Power in Predicting Demand: No More Guesswork!
One of the biggest headaches for any business is figuring out how much product to have on hand. Too much, and you’re stuck with costly, unsold inventory. Too little, and you miss out on sales and frustrate customers. AI tackles this challenge head-on:
Traditional Demand Forecasting vs. AI-Powered Prediction
- Traditional: Often relies on simple historical sales data, perhaps adjusting for seasonality. It struggles with sudden changes, new trends, or external factors.
- AI-Powered: Uses sophisticated Machine Learning (ML) algorithms to analyze a vast array of data points, far beyond just past sales.
How AI Predicts Demand: The Data & The Magic
AI’s ability to predict demand comes from its capacity to ingest and analyze diverse data sources:
- Historical Sales Data: Not just totals, but sales patterns by product, location, time of day, and even specific customer segments.
- External Factors:
- Weather Forecasts: Predicting demand for umbrellas during rainy seasons or ice cream during heatwaves.
- Economic Indicators: Understanding how consumer spending habits change with inflation or unemployment.
- Social Media Trends & News: Detecting sudden spikes in interest for a product or category based on viral content or news events.
- Competitor Activity: Analyzing what competitors are selling and at what prices.
- Marketing Campaigns: Understanding the impact of promotions and advertising on demand.
- Public Holidays & Events: Anticipating increased demand for specific products during holidays, sports events, or festivals.
- Supply Chain Data: Inventory levels, lead times, supplier performance.
By processing this data, AI can:
- Identify complex patterns: It can see subtle correlations between seemingly unrelated data points that humans would miss.
- Create dynamic forecasts: Predictions aren’t static; they continuously update as new data comes in.
- Predict demand at granular levels: Forecast demand not just for a product category, but for a specific SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) in a particular store on a given day.
Benefits of AI-Driven Demand Prediction:
- Minimized Stockouts: Ensures products are available when customers want them, preventing lost sales and customer frustration.
- Reduced Overstocking: Avoids tying up capital in excess inventory, reducing storage costs and waste.
- Improved Production Planning: Manufacturers can align production schedules more closely with actual demand, leading to more efficient resource use.
- Better Pricing Strategies: Dynamic pricing can be implemented based on predicted demand fluctuations.
- Enhanced Promotional Effectiveness: Marketing teams can plan promotions knowing the likely impact on demand.
AI’s Impact on Optimizing Logistics: Smooth Moves, Smart Deliveries
Once demand is predicted, the next challenge is getting the right products to the right place at the right time. Logistics, the art of moving things efficiently, is another area where AI shines brightly.
Key Areas Where AI Optimizes Logistics:
-
Route Optimization:
- The Challenge: Finding the most efficient paths for delivery vehicles, considering traffic, weather, road closures, delivery windows, and vehicle capacity.
- AI’s Solution: AI algorithms analyze real-time traffic data, weather conditions, historical delivery times, and even vehicle performance to recommend the quickest, most fuel-efficient routes. They can dynamically re-route vehicles if unexpected delays occur.
- Benefits: Reduces fuel consumption, cuts delivery times, lowers transportation costs, and improves fleet utilization.
-
Warehouse Management:
- The Challenge: Efficiently storing, retrieving, and preparing orders in large, complex warehouses.
- AI’s Solution:
- Optimized Layouts: AI can suggest the most efficient placement of products based on demand and picking frequency.
- Automated Picking: Robots guided by AI can pick and move items faster and more accurately than humans.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI monitors machinery (conveyor belts, forklifts) to predict when they might break down, allowing for proactive maintenance.
- Workforce Optimization: AI can schedule staff based on predicted workload.
- Benefits: Faster order fulfillment, reduced labor costs, increased accuracy, and improved safety.
-
Fleet Management:
- The Challenge: Managing a fleet of vehicles efficiently, including maintenance, fuel, and driver scheduling.
- AI’s Solution: AI monitors vehicle performance, predicts maintenance needs, optimizes fuel consumption patterns, and helps schedule drivers for maximum efficiency while adhering to regulations.
- Benefits: Extends vehicle lifespan, reduces operational costs, and ensures compliance.
-
Real-time Tracking & Visibility:
- The Challenge: Knowing exactly where a shipment is at any given moment and anticipating potential delays.
- AI’s Solution: AI integrates data from GPS, IoT sensors (Internet of Things), and external sources (weather, traffic) to provide live updates on shipment locations and estimated arrival times. It can also flag potential issues before they become major problems.
- Benefits: Improves customer service, allows for proactive problem-solving, and increases supply chain transparency.
-
Last-Mile Delivery:
- The Challenge: The most expensive and often most complex part of the delivery process – getting the product from the local hub to the customer’s door.
- AI’s Solution: AI optimizes delivery sequences for individual drivers, integrates with smart lockers or drone delivery systems, and can even help predict customer availability for delivery.
- Benefits: Faster deliveries, lower costs per delivery, and improved customer experience.
Beyond Demand & Logistics: Other AI Applications in Supply Chain
While demand prediction and logistics optimization are prime examples, AI’s influence stretches across the entire supply chain:
- Inventory Management: AI dynamically adjusts inventory levels based on real-time demand, lead times, and storage costs, minimizing holding costs and stockouts.
- Supplier Relationship Management: AI can evaluate supplier performance, identify potential risks (e.g., financial instability, ethical concerns), and even help with contract negotiations.
- Quality Control: AI-powered computer vision systems can inspect products for defects faster and more accurately than the human eye, ensuring consistent quality.
- Risk Management: AI monitors global events (political instability, natural disasters, epidemics) and assesses their potential impact on the supply chain, suggesting contingency plans.
- Sustainability: AI can optimize routes to reduce carbon emissions, identify opportunities for waste reduction, and help businesses meet their environmental goals.
How AI Works: The Simplified Tech Behind It
For beginners, understanding the "how" of AI in supply chain can seem daunting, but it boils down to a few key steps:
- Data Collection: AI needs data – lots of it! This comes from various sources: sales records, sensor data from trucks and warehouses, weather feeds, news articles, social media, and more.
- Data Processing & Cleaning: Raw data can be messy. AI systems first clean, organize, and prepare this data so it can be understood and used.
- Machine Learning (ML) Algorithms: This is the "brain" of AI. ML algorithms are sets of complex rules and statistical models that learn from the data. They look for patterns, correlations, and anomalies.
- Think of it like teaching a child: You show them many pictures of cats and dogs, and they learn to tell the difference. ML algorithms are "shown" vast amounts of data and "learn" to predict outcomes or identify patterns.
- Pattern Recognition & Prediction: Once the algorithms have "learned," they can then apply that learning to new, unseen data.
- If they’ve learned that demand for ice cream spikes when temperatures exceed 25°C, they can predict a spike in demand for ice cream when a 25°C forecast comes in.
- If they’ve learned that a particular road is always congested at 5 PM, they’ll avoid recommending that route at that time.
- Recommendations & Automation: Based on their predictions and analyses, AI systems can then:
- Recommend actions: "Increase order for product X by 15% next week." "Use Route B for delivery 123."
- Automate tasks: In some cases, if the confidence level is high and the task is routine, AI can trigger actions directly, like automatically reordering a low-stock item.
Challenges of Adopting AI in Supply Chain
While the benefits are clear, implementing AI isn’t without its hurdles:
- Data Quality & Availability: AI is only as good as the data it’s fed. Inconsistent, incomplete, or siloed data can severely limit AI’s effectiveness.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Many companies have legacy systems that aren’t designed to easily share data with new AI platforms.
- Cost of Implementation: Investing in AI technology, infrastructure, and skilled personnel can be a significant upfront expense.
- Skills Gap: A shortage of data scientists, AI engineers, and supply chain professionals who understand AI can slow adoption.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may be hesitant to adopt new technologies or fear job displacement, requiring careful change management.
- Complexity: Designing and deploying effective AI solutions requires deep expertise.
Getting Started with AI in Your Supply Chain
For businesses looking to harness the power of AI, here’s a practical approach:
- Start Small, Think Big: Don’t try to overhaul everything at once. Identify a specific, high-impact problem (e.g., reducing stockouts for a key product line, optimizing a specific delivery route) and pilot an AI solution there.
- Define Clear Goals: What do you want AI to achieve? (e.g., "Reduce inventory holding costs by 10%," "Improve on-time delivery by 5%").
- Assess Your Data: Understand what data you have, its quality, and where it resides. Data cleansing and consolidation will likely be a crucial first step.
- Seek Expertise: Partner with AI solution providers or consultants who specialize in supply chain applications. They can guide you through the process and help select the right tools.
- Pilot Projects: Test AI solutions on a smaller scale, learn from the results, and refine your approach before rolling it out more broadly.
- Train Your Team: Educate your employees about AI, how it works, and how it will benefit them and the company. Foster a culture of data-driven decision-making.
The Future of AI in Supply Chains
The journey of AI in supply chain optimization is just beginning. We can expect to see:
- Hyper-Personalization: AI will enable supply chains to cater to individual customer preferences with unprecedented precision.
- Autonomous Operations: Further automation in warehouses and even self-driving vehicles will become more common.
- Predictive Resilience: AI will become even more sophisticated at predicting and mitigating global disruptions, creating highly adaptable supply networks.
- Increased Collaboration: AI platforms will facilitate seamless data sharing and collaboration across different companies within a supply chain.
- Ethical AI: Growing focus on ensuring AI systems are fair, transparent, and used responsibly.
Conclusion
AI is no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses aiming to thrive in today’s dynamic global marketplace. By providing unparalleled insights into demand patterns and optimizing the intricate dance of logistics, AI empowers supply chains to be more efficient, cost-effective, resilient, and customer-centric. While challenges exist, the path to an AI-powered supply chain is clear, promising a future where goods move seamlessly, demand is met precisely, and disruptions are merely minor blips on the radar. Embracing AI isn’t just about adopting new technology; it’s about building a smarter, more sustainable, and ultimately more successful future for your business.


Post Comment